注解的基本结构
以重写为例子了解基本结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 package java.lang;import java.lang.annotation.*;@Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) public @interface Override {}
注解的名称:
1 2 public @interface Override {}
注解的元注解
1 2 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
这两个注解是注解中用到最多的元注解
总结:
注解分为两部分 :
元注解 ;
public @interface 注解名称 ;
注解的本质
按照 public @interface 注解名称 格式 , 写出一个注解 ,
编译该注解代码生成 Annotation.class 字节码文件 ;
1 2 public @interface Annotation {}
使用 javap 命令反编译 Annotation.class 字节码文件 ,
查看该注解的实际代码 ;
发现输出
1 2 public interface Annotation extends java .lang.annotation.Annotation {}
所以说,注解的本质是一个 interface 接口 , 注解接口默认继承了
java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口 ;
有如下关键特性:
注解接口隐式继承Annotation接口
不能显式实现其他接口
不能包含泛型参数
不能抛出异常
注解的属性
注解的属性
注解的本质是接口 , 接口中可以定义 常量 和 方法 ;
在注解中定义 接口方法 , 就是 注解的属性 ;
为注解添加属性 : 接口中的方法都是抽象方法 , 其中 public abstract
可以省略 ;
1 2 3 public @interface Annotation { public abstract String path () ; }
使用
1 2 @Annotation(path = "") Student(String name, int age){}
属性定义规则
1 2 3 4 5 public @interface RequestMapping { String path () ; String method () default "GET" ; String[] params() default {}; }
注解的属性类型
注解中定义了属性 , 在使用注解时 , 需要 给 注解属性 赋值 ;
定义 注解属性 时 , 可以 使用 default 关键字 指定属性默认值
1 int intValue () default 666 ;
如果 注解属性 指定了默认值 , 在使用注解时 , 可以选择
不为该属性赋值 ( 此时使用默认属性值 ) , 也可以进行赋值 (
指定一个新的属性值 ) ;
如果 注解属性 没有指定默认值 , 则使用 注解 时 ,
必须为其指定一个默认值 , 否则编译时报错 ;
注解属性 ( 接口方法 ) 返回值类型要求 :
基本数据类型 : byte , short , int , long , float , double , char ,
boolean ;
字符串类型 : String ;
枚举类型 : enum ;
注解类型 ;
其他注解类型
以上类型的数组形式 ,不允许多维数组
禁止的类型:
自定义对象类型
泛型类型(如List)
null值(默认值不能为null)
注解属性返回值必须是以上的类型 , 不能设置其它类型返回值 , 否则会报错
;
赋值简化操作:
如果 注解属性 名称是 value , 并且 注解中只有 1 个属性 , 那么在使用
注解 为 注解属性 赋值时 , 可以省略注解名称 , 直接传入 注解属性值 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) public @interface SuppressWarnings { String[] value(); } @SuppressWarnings("all") @Override public String toString () { return super .toString(); }
注解属性 名称是 value , 并且 注解中只有 1 个属性,
才能使用上述简化方式
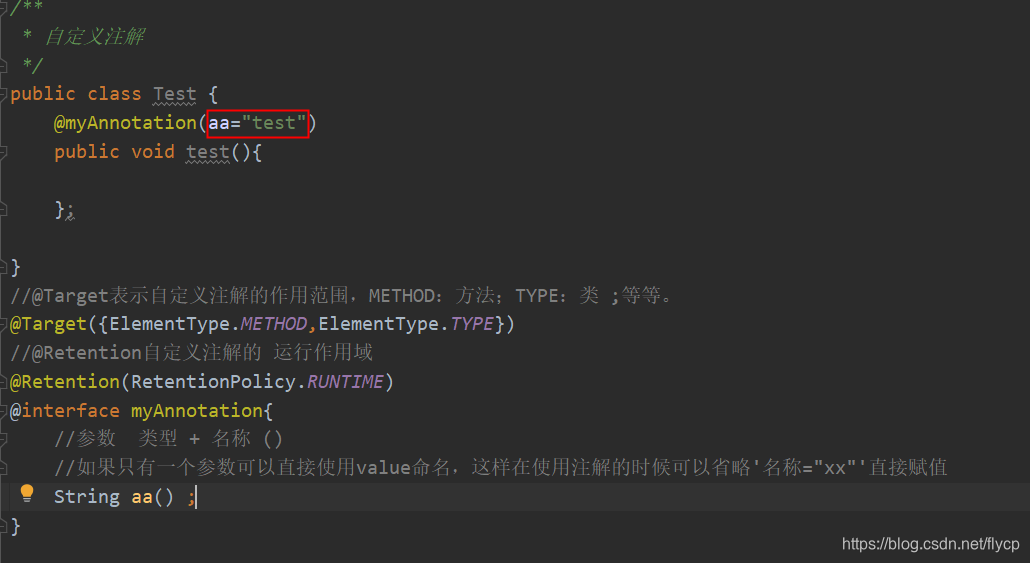
自定义一个注解
使用@interface来申明一个自定义注解时,他会自动继承ava.lang.annotation.Annotation接口。
格式public @interface
xxx(注解名称){定义注解参数内容}。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface ApiVersion { String group () default "default" ; int [] versions(); } @ApiVersion(group = "user", versions = {1, 2}) public class UserController { @ApiVersion(versions = {2}) public void updateUser () {...} } Class<UserController> clazz = UserController.class; ApiVersion classAnnotation = clazz.getAnnotation(ApiVersion.class);if (classAnnotation != null ) { System.out.println("Supported versions: " + Arrays.toString(classAnnotation.versions())); }
如果是注解有参数,需要在注解里面添加参数类型
参数格式: 类型 + 名称();
加了参数后,使用注解如果不添加参数的话会报错,除非添加默认值
参数设计建议
当只有一个参数时,建议命名为value
数组参数建议提供空数组默认值(default {})
复杂参数使用注解嵌套:
111
如果只有一个参数可以直接使用value命名,这样在使用注解的时候可以省略’名称=“xx”’直接赋值
注解的使用
自定义注解的使用需要用到反射的原理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface ClassAnno{ String value () ; } @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface FiledAnnoName{ String name () ; } @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface FiledAnnoAge{ int age () ; } public class CustomAnnotationExample { public static void main (String[] args) { Class<Person> personClass = Person.class; if (personClass.isAnnotationPresent(ClassAnno.class)) { ClassAnno classAnno = personClass.getAnnotation(ClassAnno.class); System.out.println("类注解信息: " + classAnno.value()); } Field[] fields = personClass.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { if (field.isAnnotationPresent(FiledAnnoName.class)) { FiledAnnoName filedAnnoName = field.getAnnotation(FiledAnnoName.class); System.out.println("属性 " + field.getName() + " 的注解信息: " + filedAnnoName.name()); } if (field.isAnnotationPresent(FiledAnnoAge.class)) { FiledAnnoAge filedAnnoAge = field.getAnnotation(FiledAnnoAge.class); System.out.println("属性 " + field.getName() + " 的注解信息: " + filedAnnoAge.age()); } } }
引用
【Java
注解】自定义注解 ( 注解属性定义与赋值 )
java如何优雅的自定义一个注解?