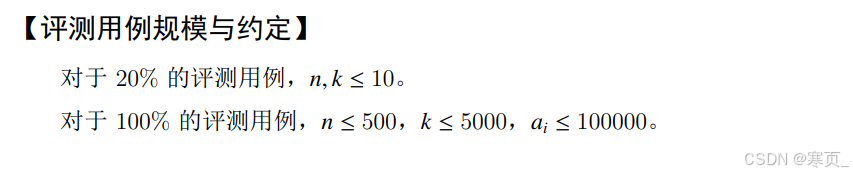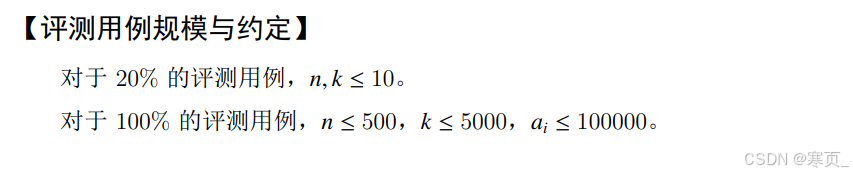由于河北北京这边省赛那两天风很大的原因,所以导致蓝桥杯没有如期进行,所以说来做做已经考完了的人的比赛题目
A. 逃离高塔
 A
A
 A
A
首先如果不考虑溢出处理,用BigInteger估计一是比较慢二是方法写起来比较麻烦,所以还是取模取出个位数处理,因为只看个位数,所以取模不会对结果产生影响
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 2025; i++) {
int temp = (int) (((Math.pow(i, 2) % 10) * i) % 10);
if(temp == 3) res++;
}
System.out.print(res);
}
}
|
B. 消失的蓝宝
 img
img
 img
img
大模拟题,首先 N 肯定是从
20250413开始遍历,但是直接遍历肯定要慢很多
可以先打表发现,20260411 是第一个满足条件2 的数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public class B {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long res = 0;
for(long n = 20250413; n < Long.MAX_VALUE; n++) {
if((n + 20250412) % 20240413 == 0) {
res = n;
break;
}
if((n + 20240413) % 20250412 == 0) {
res = n;
break;
}
}
System.out.print(res);
}
}
|
所以从 20260411 开始,每次加 20250412
确保满足条件2,然后判断条件1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class B {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long res = 0;
for (long N = 20260411; N < Long.MAX_VALUE; N += 20250412) {
if ((N + 20250412) % 20240413 == 0) {
res = N;
break;
}
}
System.out.print(res);
}
}
|
C. 电池分组
 C
C
 C
C
 img
img
 img
img
两组电池异或和相等,异或 相同为
0,不同为1,那么相等的数异或和为 0,要求能分成两组,
那么就是意思组内所有数异或后为 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class C {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
int sum = 0;
int N = sc.nextInt();
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
int element = sc.nextInt();
sum = sum ^ element;
}
if(sum == 0) {
System.out.println("YES");
}else {
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
}
}
|
D. 魔法科考试
 image-20250419141858122
image-20250419141858122
 image-20250419141858122
image-20250419141858122
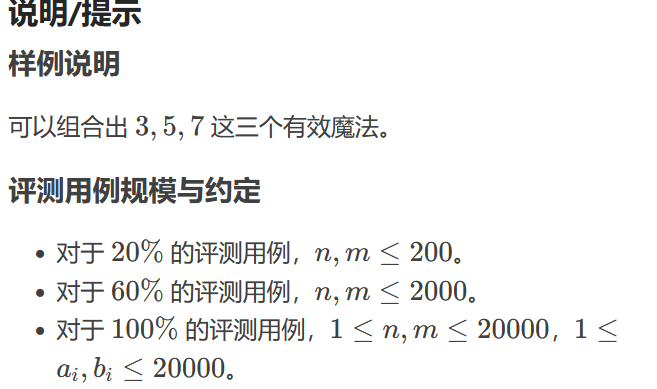 image-20250419141915330
image-20250419141915330
 image-20250419141915330
image-20250419141915330
朴素模拟发现只能过2/ 5的数据,那么该如何优化呢
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| class Solutions1{
boolean check(int p) {
for(int i = 2; i * i <= p; i++) {
if(p % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
public Solutions1() {
FastReader sc = new FastReader();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(a);
Arrays.sort(b);
int index_a = 0 ,index_b = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(a[i] > n + m) break;
index_a++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if(b[i] > n + m) break;
index_b++;
}
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < index_a; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < index_b; j++) {
if(a[i] + b[j] <= m + n && check(a[i] + b[j])) {
set.add(a[i] + b[j]);
}
}
}
System.out.println(set.size());
}
|
首先,看到时间限制就知道这题不简单。
我们在这里要注意以下几个点
- 素数判定只需要判定这个数的算术平方根及以下的数是不是这个数的因数,这样更节省时间。
- 对于已经判定过的数,不需要判断,所以可以打质数筛
if
判断是有顺序的(从左往右判断)所以素数判定放在最后,当前面不符时,会直接退出就不会再素数判定,节省时间。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
|
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Solutions1();
}
}
class Solutions1{
int[] dx = new int[40004];
boolean check(int p) {
if(dx[p] == 1) return false;
if(dx[p] == 2) return true;
for(int i = 2; i * i <= p; i++) {
if(p % i == 0) {
dx[p] = 1;
return false;
}
}
dx[p] = 2;
return true;
}
public Solutions1() {
FastReader sc = new FastReader();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(a);
Arrays.sort(b);
int index_a = 0 ,index_b = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(a[i] > n + m) break;
index_a++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if(b[i] > n + m) break;
index_b++;
}
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < index_a; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < index_b; j++) {
if(a[i] + b[j] <= m + n && check(a[i] + b[j])) {
set.add(a[i] + b[j]);
}
}
}
System.out.println(set.size());
}
class FastReader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastReader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
}
String next() {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
|
E. 爆破
 img
img
 img
img
 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述
 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述
题目大意:使用尽可能的小距离使 n 个圆连在一起。
最小生成树,圆和圆的距离可以用圆心距离减半径,用 prim
写吧,算法讲解都在注释里详细写下了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Solutions();
}
}
class Solutions {
private int n;
private class cirlce implements Comparable<cirlce> {
int x, y, r;
public cirlce() {
}
public cirlce(int x, int y, int r) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.r = r;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(cirlce o) {
return this.x - o.x;
}
}
private cirlce[] cirlces = new cirlce[5005];
private double Getdist(int u, int v) {
return Math.sqrt((cirlces[u].x - cirlces[v].x) * (cirlces[u].x - cirlces[v].x) + (cirlces[u].y - cirlces[v].y) * (cirlces[u].y - cirlces[v].y));
}
private double prim() {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
double[] dist = new double[n];
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
Arrays.fill(dist, Double.MAX_VALUE);
dist[0] = 0.0;
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int u = -1;
double minDist = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(!visited[j] && dist[j] < minDist){
minDist = dist[j];
u = j;
}
}
if(u == -1){
break;
}
visited[u] = true;
sum += minDist;
for(int v = 0; v < n; v++){
if(!visited[v]){
double w;
double spcr = Getdist(u, v);
if(spcr <= cirlces[u].r + cirlces[v].r){
w = 0.0;
}else{
w = spcr - (cirlces[u].r + cirlces[v].r);
}
if(w < dist[v]){
dist[v] = w;
}
}
}
}
return sum;
}
public Solutions() {
FastReader sc = new FastReader();
n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cirlces[i] = new cirlce(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
}
double sum = prim();
System.out.printf("%.2f", sum);
}
class FastReader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastReader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
}
public String next() {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
|
F. 数组翻转
 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述
 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述
 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述
 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述
贪心,可以发现,答案只跟数组中每个数连续出现的次数有关,如果有两段一样且连续的数但是被分隔开了,那么肯定存在一种翻转方法翻转到答案的数值,所以答案就是统计这两段然后一乘
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Solutions();
}
}
class Solutions {
public Solutions() {
FastReader in = new FastReader();
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
for (int a_i = 0; a_i < n; a_i++) {
a[a_i] = in.nextInt();
}
int[][] backet = new int[1000086][2];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int cp = 0;
cp++;
while(i < n - 1 && a[i] == a[i + 1]){
cp++;
i++;
}
if(cp > backet[a[i]][0]){
backet[a[i]][1] = backet[a[i]][0];
backet[a[i]][0] = cp;
}else if(cp > backet[a[i]][1]){
backet[a[i]][1] = cp;
}
}
long res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 1000003; i++){
long temp = (long) i * (backet[i][1] + backet[i][0]);
if(temp > res){
res = temp;
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
class FastReader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastReader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
}
public String next() {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
|
G. 2的幂
 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述
 在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述
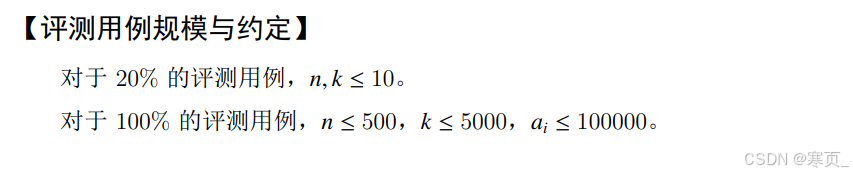 img
img
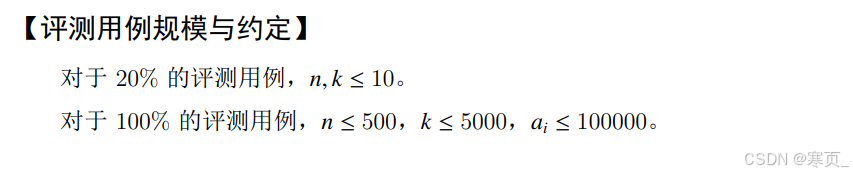 img
img
数组中所有元素的乘积是 2 的 k 次方倍数。
- 要做到这一点,数组中所有元素的 2 的幂次之和必须至少为 k。
如果数组中所有元素的 2 的幂次之和大于k,已经符合了,输出0
如果初始的 2 的幂次之和小于
k,则需要通过重新选择或增加数组中的某些元素,来使总的 2 的幂次之和达到
k。
考虑dp
- 使用一个 DP 数组 dp,其中 dp[j] 表示在增加的 2 的幂次之和为 j
时,所需的最小增加的数的总和。
- 遍历数组中的每个数 num,计算其在加上某个正整数后,新数能被 2 的 q
次方整除的最小增量cost,并且能够获得的 2 的幂次增量 gain。
- 更新 DP 数组,即通过考虑当前数的所有可能增加的选项来更新之前的 DP
状态。
- 如果 dp[re](其中 re 是需要补充的 2
的幂次)仍然是无穷大,说明无法达到目标,输出 -1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
| package 动态规划.subject.线性dp.P12160_蓝桥杯2025省JavaB_2的幂;
import scala.reflect.internal.util.OwnerOnlyChmod;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Solutions();
}
}
class Solutions{
private int countTwos(int num) {
int count = 0;
while(num % 2 == 0 && num > 0){
count++;
num /= 2;
}
return count;
}
public Solutions(){
FastReader fs = new FastReader();
int n = fs.nextInt();
int k = fs.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = fs.nextInt();
int total = 0;
for(int num: a){
total += countTwos(num);
}
if(total >= k){
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
int rp = k - total;
int[] dp = new int[rp + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int num = a[i];
int p = countTwos(num);
int[] tempDp = dp.clone();
for (int q = p + 1; q <= 30; q++) {
long mp = (long)Math.pow(2, q);
if(mp > 100000) break;
long sp = ((long)num + mp - 1) / mp * mp;
int cost = (int)(sp - num);
int gain = countTwos((int)sp) - p;
if (gain <= 0) continue;
for(int j = rp; j >= gain; j--){
if(dp[j - gain] != Integer.MAX_VALUE){
tempDp[j] = Math.min(tempDp[j], dp[j - gain] + cost);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(dp[rp] == Integer.MAX_VALUE? -1 : dp[rp]);
}
class FastReader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastReader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
}
public String next() {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
|
H. 研发资源分配
 img
img
 img
img
 img
img
 img
img
可以发现,题目思路类似于田忌赛马,贪心考虑,用下等马换掉对方的上等马
例如题解 1 3 2 用 2 1 3,就是用 最下等的 1 抵掉了 最上等的 3
而且由于是全排列,所以剩下的所有位置一定可以排出都比对方大的排列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Solutions2();
}
}
class Solutions2{
public Solutions2(){
FastReader sc = new FastReader();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] b = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) b[i] = sc.nextInt();
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
long res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(b[i] == n){
res -= i;
}else{
res += i;
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
class FastReader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastReader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer("");
}
public String next() {
while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
}
}
|
 image-20250419164239152
image-20250419164239152
 image-20250419164239152
image-20250419164239152