Spring Boot 的缓存机制
随着应用用户量的不断增长和数据规模的持续扩大,数据库查询操作往往成为影响用户体验的关键瓶颈。缓存作为一种高效的解决方案,能够显著提升系统性能。Spring
Boot
提供了强大的缓存支持,通过基于注解的低侵入式方式,帮助开发者轻松地为应用添加缓存功能。
Spring Boot 中的缓存机制原理
缓存抽象层
Spring Boot 的缓存机制基于 Spring
框架的缓存抽象,它提供了一套统一的接口和注解,使得开发者可以在不关心具体缓存实现的情况下使用缓存功能。这种抽象层的设计,让开发者能够灵活地切换不同的缓存技术,如
Redis、Ehcache 等。
Spring
从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;同时支持JCache(JSR-107)注解。
工作原理
Spring 缓存机制基于
AOP(面向切面编程)实现,通过动态代理在方法执行前后添加缓存逻辑:
方法调用前:检查缓存中是否存在对应的数据
缓存命中:直接返回缓存数据,跳过方法执行
缓存未命中:执行目标方法,将结果存储到缓存中
方法调用后:根据配置更新或清除缓存
Spring Boot 中的缓存支持
Spring Boot
提供了开箱即用的缓存抽象层,使得开发者能够轻松地集成各种缓存解决方案。Spring
Cache
抽象主要基于注解配置,提供了统一的编程模型来操作不同类型的缓存后端。
要启用 Spring Boot 的缓存支持,只需在主配置类或
application.properties 文件中添加以下配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
|
或者在 application.properties 中设置:
1
| spring.cache.type=simple # 简单内存缓存,可以用 Redis、Ehcache 等
|
HTTP缓存
HTTP
缓存是浏览器缓存体系的重要组成部分,浏览器缓存也包含很多内容:HTTP缓存、indexDB、缓存、本地存储等等,主要通过两种核心机制实现资源缓存控制:
浏览器主要分为Last-Modified/Etag和Cache-Control/Expires
- 协商缓存(Conditional
Cache):通过
Last-Modified/Etag实现,需与服务器确认资源是否更新
- 强缓存(Strict
Cache):通过
Cache-Control/Expires实现,直接根据本地缓存时间判断是否可用
协商缓存机制:Last-Modified
与 Etag
Last-Modified
工作原理
基本概念:服务器响应请求时,在响应头中添加Last-Modified字段,标识资源最后修改时间。
交互流程:
- 首次请求:服务器返回资源及
Last-Modified: Fri, 28 May 2025 12:00:00 GMT
- 后续请求:浏览器自动在请求头中添加
If-Modified-Since字段(值为上次的
Last-Modified)
- 服务器对比时间:
- 若资源未修改:返回
304 Not Modified,浏览器使用本地缓存
- 若资源已修改:返回
200 OK及最新资源
Etag 工作原理
基本概念:服务器为资源生成唯一标识(类似哈希值),存储在Etag响应头中。
交互流程:
- 首次请求:服务器返回
Etag: "abc123def456"
- 后续请求:浏览器在请求头中添加
If-None-Match: "abc123def456"
- 服务器验证:
- 若 Etag 匹配:返回
304 Not Modified
- 若 Etag 不匹配:返回
200 OK及新资源
优先级:Etag > Last-Modified(服务器同时存在时优先验证
Etag)
强缓存机制:Cache-Control 与
Expires
Cache-Control 核心字段
基本概念:通过响应头Cache-Control设置缓存策略,优先级高于Expires,支持更灵活的参数。
常用参数:
| 参数名 |
说明 |
示例 |
max-age=秒数 |
资源在本地缓存的最大时间(秒),超过后失效 |
Cache-Control: max-age=3600 |
s-maxage=秒数 |
共享缓存(如 CDN)的最大缓存时间,优先级高于 max-age |
Cache-Control: s-maxage=86400 |
public |
资源可被客户端和代理服务器缓存 |
Cache-Control: public |
private |
资源仅可被客户端缓存(默认值) |
Cache-Control: private |
no-cache |
强制每次请求都向服务器验证资源(并非不缓存,而是需先验证) |
Cache-Control: no-cache |
no-store |
禁止任何形式的缓存(最严格策略) |
Cache-Control: no-store |
must-revalidate |
缓存过期后必须向服务器验证,不能直接使用本地缓存 |
Cache-Control: must-revalidate |
Expires 工作原理
基本概念:服务器返回资源时,在响应头中添加Expires字段,标识资源过期的绝对时间。
交互流程:
- 首次请求:服务器返回
Expires: Fri, 29 May 2025 12:00:00 GMT
- 浏览器对比本地时间:
- 未超过时间:直接使用缓存,无需请求服务器
- 超过时间:发送请求获取新资源
核心组件
Cache 接口
Cache 接口是 Spring
缓存抽象的核心,定义了缓存的基本操作:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public interface Cache {
String getName();
Object getNativeCache();
ValueWrapper get(Object key);
<T> T get(Object key, Class<T> type);
<T> T get(Object key, Callable<T> valueLoader);
void put(Object key, @Nullable Object value);
void evict(Object key);
void clear();
}
|
CacheManager 接口
CacheManager 负责管理多个 Cache 实例:
1
2
3
4
5
| public interface CacheManager {
@Nullable
Cache getCache(String name);
Collection<String> getCacheNames();
}
|
Cache 注解详解
@EnableCaching
启用 Spring Boot 缓存功能的核心注解,需要在配置类上添加:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
|
@Cacheable
用于声明一个方法的返回值可以被缓存,是最常用的缓存注解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Service
public class UserService {
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#id")
public User getUserById(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id);
}
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#name", condition = "#name.length() > 2")
public User getUserByName(String name) {
return userRepository.findByName(name);
}
}
|
主要属性:
value/cacheNames:缓存名称,可以指定多个key:缓存的键,支持 SpEL 表达式condition:缓存条件,满足条件才缓存unless:排除条件,满足条件不缓存keyGenerator:自定义键生成器cacheManager:指定缓存管理器sync:是否同步执行
@CachePut
无论方法是否被调用过,都会执行方法体,并将结果存入缓存:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @CachePut(value = "users", key = "#user.id")
public User updateUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@CachePut(value = "users", key = "#result.id", condition = "#result != null")
public User createUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
|
updateUser 方法
- 当更新用户时,根据传入的
user.id
找到缓存中的对应条目,并用新的 user 对象替换。
- 适用于已知数据 ID 的更新场景。
createUser 方法
- 当创建用户后,根据返回的
result.id(通常是数据库生成的主键)作为键,将新用户存入缓存。
condition
确保只有创建成功(返回非空)时才更新缓存。
注解属性说明
value:标识缓存的存储位置,缓存名称需在配置中提前定义,通过
@CacheConfig 或 XML 配置key:缓存的键,唯一标识缓存数据,支持 SpEL 表达式condition:缓存条件,满足条件才缓存
@CacheEvict
用于清除缓存数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
@CacheEvict(value = "users", key = "#id")
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
userRepository.deleteById(id);
}
@CacheEvict(value = "users", allEntries = true)
public void deleteAllUsers() {
userRepository.deleteAll();
}
@CacheEvict(value = "users", key = "#id", beforeInvocation = true)
public void deleteUserWithException(Long id) {
throw new RuntimeException("删除失败");
}
|
主要属性:
allEntries:是否清除所有缓存条目beforeInvocation:是否在方法执行前清除缓存
@CacheConfig
类级别的缓存配置,用于设置该类中所有缓存操作的默认配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "users", keyGenerator = "customKeyGenerator")
public class UserService {
@Cacheable
public User getUserById(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id);
}
}
|
SpEL 表达式在缓存中的应用
SpEL(Spring Expression Language)是Spring框架中用于表达式语言的一种方式。它类似于其他编程语言中的表达式语言,用于在运行时计算值或执行特定任务。
SpEL表达式可以在字符串中进行定义,使用特殊的语法和符号来表示特定的操作。
SpEL支持各种操作和函数,包括算术运算、逻辑运算、条件判断、正则表达式匹配、集合操作等。它还支持访问上下文中的变量和参数,以及调用对象的方法。
Spring 缓存支持强大的 SpEL(Spring Expression Language)表达式:
可用变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| public class CacheExample {
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#id")
public User getUser(Long id) { ... }
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#user.id")
public User saveUser(User user) { ... }
@CachePut(value = "users", key = "#result.id")
public User updateUser(User user) { ... }
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#root.methodName + '_' + #id")
public User findUser(Long id) { ... }
@Cacheable(value = "users", condition = "#id > 0 and #id < 1000")
public User getUserInRange(Long id) { ... }
@Cacheable(value = "users",
key = "#user.id",
condition = "#user.age >= 18",
unless = "#result == null or #result.status == 'INACTIVE'")
public User getActiveAdultUser(User user) { ... }
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#user?.id", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUser(User user) { ... }
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#product.generateCacheKey()")
public Product getProduct(Product product) { ... }
@Cacheable(value = "config", key = "T(java.util.UUID).randomUUID().toString()")
public Config getDynamicConfig() { ... }
}
|
自定义键生成器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @Component
public class CustomKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
StringBuilder key = new StringBuilder();
key.append(target.getClass().getSimpleName()).append("_");
key.append(method.getName()).append("_");
for (Object param : params) {
if (param != null) {
key.append(param.toString()).append("_");
}
}
return key.toString();
}
}
|
Spring Boot
使用自带缓存机制的例子
在 pom.xml 中添加如下依赖(Spring Boot Starter Cache):
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
实体类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
public class Product implements Serializable {
private String id;
private String name;
private double price;
}
|
服务层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class ProductService {
private Map<String, Product> productMap = new HashMap<>();
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#id")
public Product getProductById(String id) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return productMap.get(id);
}
public void addProduct(Product product) {
productMap.put(product.getId(), product);
}
@CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "#id")
public void deleteProduct(String id) {
productMap.remove(id);
}
}
|
控制器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/products")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Product getProduct(@PathVariable String id) {
return productService.getProductById(id);
}
@PostMapping
public void addProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
productService.addProduct(product);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void deleteProduct(@PathVariable String id) {
productService.deleteProduct(id);
}
}
|
启动类,需要加上 @EnableCaching 注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class CacheDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
可以进行一些常用的缓存配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
spring.cache.type=simple
spring.cache.cache-names=products,users
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=3600000
spring.cache.cache-null-values=true
spring.cache.jcache.provider=com.example.MyCacheProvider
spring.cache.redis.use-key-prefix=true
spring.cache.redis.key-prefix=mycache:
spring.cache.redis.cache-null-values=true
spring.cache.redis.expires=3600
spring.cache.ehcache.config=classpath:ehcache.xml
spring.cache.override-spring-cache-config=false
spring.cache.cache-manager=com.example.MyCacheManagerImpl
spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.cache.redis.serialization-mode=json
spring.cache.cache-statistics-enabled=true
|
或者就是写缓存的配置类了 需要标注 @Configuration
和@EnableCaching 注解
常用的 HTTP 请求状态码
在这里提一下上一篇忘提到的状态码
信息性状态码(100 - 199)
表示服务器已接收请求,正在处理中。
- 100 Continue
客户端发送了部分请求,服务器指示可继续发送剩余内容。
- 101 Switching Protocols
服务器接受协议切换请求(如从 HTTP 切换到 WebSocket)。
- 103 Early Hints
服务器提前返回资源提示(如预加载响应头),优化用户体验。
成功状态码(200 - 299)
表示请求已成功处理。
- 200 OK
最常见的成功响应,请求已完成且资源正常返回。
- 201 Created
请求创建了新资源(如上传文件、创建用户),返回资源位置。
- 202 Accepted
请求已接受但尚未完成处理(如异步任务)。
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information
服务器返回的信息并非来自原始数据源(如缓存)。
- 204 No Content
请求成功但无返回内容(如删除操作后),浏览器不刷新页面。
- 205 Reset Content
请求成功,客户端需重置文档视图(如表单重置)。
- 206 Partial Content
服务器返回部分资源(如大文件分片下载),配合
Range请求头使用。
重定向状态码(300 - 399)
表示需要客户端进一步操作以完成请求。
- 301 Moved Permanently
资源永久迁移,后续请求应使用新 URL(SEO 需注意更新链接)。
- 302 Found 资源临时迁移,客户端应使用原 URL
重新请求(如登录页重定向)。
- 303 See Other 请求的响应需重定向到其他
URL(通常用于 POST 请求后的跳转)。
- 304 Not Modified
资源未修改,客户端可使用缓存内容(减少带宽消耗)。
- 307 Temporary Redirect
临时重定向,保留原始请求方法(如 POST 请求重定向后仍为 POST)。
- 308 Permanent Redirect
永久重定向,保留原始请求方法(替代 301,更规范)。
客户端错误状态码(400 - 499)
表示客户端请求存在错误。
- 400 Bad Request 请求语法错误(如参数格式错误、JSON
解析失败)。
- 401 Unauthorized 未授权,需提供认证信息(如
Token、Cookie)。
- 402 Payment Required
预留状态码(理论上用于付费场景,实际很少使用)。
- 403 Forbidden 服务器拒绝请求(如权限不足、IP
被封禁)。
- 404 Not Found 资源不存在(URL
错误或资源已删除)。
- 405 Method Not Allowed
请求方法不被允许(如对静态资源使用 POST 请求)。
- 406 Not Acceptable
服务器无法提供符合
Accept头要求的响应格式。
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
需要代理服务器认证(与 401 类似,但针对代理)。
- 408 Request Timeout
请求超时,服务器未在规定时间内收到完整请求。
- 409 Conflict
请求与资源状态冲突(如版本冲突、重复提交)。
- 410 Gone 资源永久删除(比 404
更明确,提示不再存在)。
- 411 Length Required
请求缺少
Content-Length头(需指定请求体长度)。
- 412 Precondition Failed
请求的条件(如
If-Modified-Since)不满足。
- 413 Payload Too Large
请求体过大,超出服务器限制(如文件上传大小超限)。
- 414 URI Too Long URL
过长,服务器无法处理(常见于携带过多参数)。
- 415 Unsupported Media Type 请求体格式不支持(如发送
JSON 但未声明
Content-Type: application/json)。
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
请求的
Range范围无效(如超出文件大小)。
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
请求格式正确但语义错误(如表单验证失败,REST API 常用)。
- 425 Too Early
请求过早,服务器拒绝处理(如防止重放攻击)。
- 426 Upgrade Required 服务器要求升级协议(如从 HTTP
升级到 HTTPS)。
- 428 Precondition Required
请求需包含条件头(如
If-Match,用于乐观锁)。
- 429 Too Many Requests
客户端请求频率过高,触发限流(如 API 访问频次限制)。
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large
请求头字段过大,服务器拒绝处理。
服务器错误状态码(500 - 599)
表示服务器处理请求时发生错误。
- 500 Internal Server Error
最常见的服务器错误(如代码异常、数据库连接失败)。
- 501 Not Implemented 服务器不支持请求的功能(如未知
API 接口)。
- 502 Bad Gateway
代理服务器从上游服务器获取响应失败(如 Nginx 后端服务异常)。
- 503 Service Unavailable
服务器暂时不可用(如过载、维护中,常伴随
Retry-After头)。
- 504 Gateway Timeout
代理服务器等待上游服务器响应超时。
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported 服务器不支持请求的
HTTP 版本(如使用 HTTP/3 但服务器未启用)。
- 511 Network Authentication Required
客户端需进行网络认证(如公共 WiFi 的登录页)。
记忆技巧
- 2xx:成功(200 OK 是核心)。
- 3xx:重定向(301 永久、302 临时)。
- 4xx:客户端错(404 找不到、403 没权限)。
- 5xx:服务器错(500 内部错误、502 网关错误)。
Spring Boot 下控制和配置缓存
spring.web 下都有什么配置
- 国际化相关配置
locale:用于设置应用程序的默认区域设置。例如,可以设置为Locale.US或Locale.CHINA等,以指定应用程序的默认语言和地区。localeResolver:指定用于解析用户请求中的区域设置的策略。可取值为FIXED(固定的区域设置)或ACCEPT_HEADER(根据请求头中的Accept-Language字段来解析区域设置)。
- 静态资源的相关配置策略(开启,处理链,缓存)
resources.staticLocations:指定静态资源的位置。默认值为classpath:/META - INF/resources/、classpath:/resources/、classpath:/static/、classpath:/public/,可以通过设置此属性来添加或修改静态资源的位置。resources.addMappings:是否自动添加静态资源的映射。默认为true,即
Spring 会自动将静态资源路径映射到对应的
URL,以便能够通过浏览器访问静态资源。resources.chain.enabled:资源处理链是否启用。可通过resources.chain.strategy.fixed.enabled和resources.chain.strategy.content.enabled以及此属性共同确定最终是否启用。resources.chain.cache:是否启用资源缓存,默认为true。resources.chain.compressed:是否对资源进行压缩,默认为false。resources.cache.period:静态资源缓存的时长。resources.cache.useLastModified:是否使用Last - Modified头来判断资源是否过期,默认为true。resources.cache.cachecontrol.maxAge:缓存的最大年龄,即资源在缓存中可以存在的最长时间。resources.cache.cachecontrol.noCache:是否设置Cache - Control头为no - cache,表示不使用缓存。resources.cache.cachecontrol.noStore:是否设置Cache - Control头为no - store,表示不存储缓存。resources.cache.cachecontrol.mustRevalidate:是否设置Cache - Control头的must - revalidate属性,指示缓存必须在使用之前重新验证。resources.cache.cachecontrol.noTransform:是否设置Cache - Control头的no - transform属性,防止中间缓存对资源进行转换。resources.cache.cachecontrol.cachePublic:是否设置Cache - Control头的public属性,指示缓存可以被公共缓存(如代理服务器)缓存。resources.cache.cachecontrol.cachePrivate:是否设置Cache - Control头的private属性,指示缓存只能被私有缓存(如浏览器)缓存。resources.cache.cachecontrol.proxyRevalidate:是否设置Cache - Control头的proxy - revalidate属性,指示代理服务器必须在使用缓存之前重新验证资源。resources.cache.cachecontrol.staleWhileRevalidate:设置Cache - Control头的stale - while - revalidate属性,指定在重新验证资源期间可以使用过期缓存的时长。resources.cache.cachecontrol.staleIfError:设置Cache - Control头的stale - if - error属性,指定在发生错误时可以使用过期缓存的时长。resources.cache.cachecontrol.sMaxAge:设置Cache - Control头的s - maxage属性,指定公共缓存中资源的最大缓存时间。
涉及到spring.web的配置类WebProperties源码
源码其实很长,与spring.web相关的配置类是WebProperties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
|
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.PropertyMapper;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DurationUnit;
import org.springframework.http.CacheControl;
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.web")
public class WebProperties {
private Locale locale;
private LocaleResolver localeResolver;
private final Resources resources;
public WebProperties() {
this.localeResolver = WebProperties.LocaleResolver.ACCEPT_HEADER;
this.resources = new Resources();
}
public Locale getLocale() {
return this.locale;
}
public void setLocale(Locale locale) {
this.locale = locale;
}
public LocaleResolver getLocaleResolver() {
return this.localeResolver;
}
public void setLocaleResolver(LocaleResolver localeResolver) {
this.localeResolver = localeResolver;
}
public Resources getResources() {
return this.resources;
}
public static enum LocaleResolver {
FIXED,
ACCEPT_HEADER;
private LocaleResolver() {
}
}
public static class Resources {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"};
private String[] staticLocations;
private boolean addMappings;
private boolean customized;
private final Chain chain;
private final Cache cache;
public Resources() {
this.staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
this.addMappings = true;
this.customized = false;
this.chain = new Chain();
this.cache = new Cache();
}
public String[] getStaticLocations() {
return this.staticLocations;
}
public void setStaticLocations(String[] staticLocations) {
this.staticLocations = this.appendSlashIfNecessary(staticLocations);
this.customized = true;
}
private String[] appendSlashIfNecessary(String[] staticLocations) {
String[] normalized = new String[staticLocations.length];
for(int i = 0; i < staticLocations.length; ++i) {
String location = staticLocations[i];
normalized[i] = location.endsWith("/") ? location : location + "/";
}
return normalized;
}
public boolean isAddMappings() {
return this.addMappings;
}
public void setAddMappings(boolean addMappings) {
this.customized = true;
this.addMappings = addMappings;
}
public Chain getChain() {
return this.chain;
}
public Cache getCache() {
return this.cache;
}
public boolean hasBeenCustomized() {
return this.customized || this.getChain().hasBeenCustomized() || this.getCache().hasBeenCustomized();
}
public static class Chain {
boolean customized = false;
private Boolean enabled;
private boolean cache = true;
private boolean compressed = false;
private final Strategy strategy = new Strategy();
public Chain() {
}
public Boolean getEnabled() {
return getEnabled(this.getStrategy().getFixed().isEnabled(), this.getStrategy().getContent().isEnabled(), this.enabled);
}
private boolean hasBeenCustomized() {
return this.customized || this.getStrategy().hasBeenCustomized();
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
this.customized = true;
}
public boolean isCache() {
return this.cache;
}
public void setCache(boolean cache) {
this.cache = cache;
this.customized = true;
}
public Strategy getStrategy() {
return this.strategy;
}
public boolean isCompressed() {
return this.compressed;
}
public void setCompressed(boolean compressed) {
this.compressed = compressed;
this.customized = true;
}
static Boolean getEnabled(boolean fixedEnabled, boolean contentEnabled, Boolean chainEnabled) {
return !fixedEnabled && !contentEnabled ? chainEnabled : Boolean.TRUE;
}
public static class Strategy {
private final Fixed fixed = new Fixed();
private final Content content = new Content();
public Strategy() {
}
public Fixed getFixed() {
return this.fixed;
}
public Content getContent() {
return this.content;
}
private boolean hasBeenCustomized() {
return this.getFixed().hasBeenCustomized() || this.getContent().hasBeenCustomized();
}
public static class Fixed {
private boolean customized = false;
private boolean enabled;
private String[] paths = new String[]{"/**"};
private String version;
public Fixed() {
}
public boolean isEnabled() {
return this.enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.customized = true;
this.enabled = enabled;
}
public String[] getPaths() {
return this.paths;
}
public void setPaths(String[] paths) {
this.customized = true;
this.paths = paths;
}
public String getVersion() {
return this.version;
}
public void setVersion(String version) {
this.customized = true;
this.version = version;
}
private boolean hasBeenCustomized() {
return this.customized;
}
}
public static class Content {
private boolean customized = false;
private boolean enabled;
private String[] paths = new String[]{"/**"};
public Content() {
}
public boolean isEnabled() {
return this.enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.customized = true;
this.enabled = enabled;
}
public String[] getPaths() {
return this.paths;
}
public void setPaths(String[] paths) {
this.customized = true;
this.paths = paths;
}
private boolean hasBeenCustomized() {
return this.customized;
}
}
}
}
public static class Cache {
private boolean customized = false;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS)
private Duration period;
private final Cachecontrol cachecontrol = new Cachecontrol();
private boolean useLastModified = true;
public Cache() {
}
public Duration getPeriod() {
return this.period;
}
public void setPeriod(Duration period) {
this.customized = true;
this.period = period;
}
public Cachecontrol getCachecontrol() {
return this.cachecontrol;
}
public boolean isUseLastModified() {
return this.useLastModified;
}
public void setUseLastModified(boolean useLastModified) {
this.useLastModified = useLastModified;
}
private boolean hasBeenCustomized() {
return this.customized || this.getCachecontrol().hasBeenCustomized();
}
public static class Cachecontrol {
private boolean customized = false;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS)
private Duration maxAge;
private Boolean noCache;
private Boolean noStore;
private Boolean mustRevalidate;
private Boolean noTransform;
private Boolean cachePublic;
private Boolean cachePrivate;
private Boolean proxyRevalidate;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS)
private Duration staleWhileRevalidate;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS)
private Duration staleIfError;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS)
private Duration sMaxAge;
public Cachecontrol() {
}
public Duration getMaxAge() {
return this.maxAge;
}
public void setMaxAge(Duration maxAge) {
this.customized = true;
this.maxAge = maxAge;
}
public Boolean getNoCache() {
return this.noCache;
}
public void setNoCache(Boolean noCache) {
this.customized = true;
this.noCache = noCache;
}
public Boolean getNoStore() {
return this.noStore;
}
public void setNoStore(Boolean noStore) {
this.customized = true;
this.noStore = noStore;
}
public Boolean getMustRevalidate() {
return this.mustRevalidate;
}
public void setMustRevalidate(Boolean mustRevalidate) {
this.customized = true;
this.mustRevalidate = mustRevalidate;
}
public Boolean getNoTransform() {
return this.noTransform;
}
public void setNoTransform(Boolean noTransform) {
this.customized = true;
this.noTransform = noTransform;
}
public Boolean getCachePublic() {
return this.cachePublic;
}
public void setCachePublic(Boolean cachePublic) {
this.customized = true;
this.cachePublic = cachePublic;
}
public Boolean getCachePrivate() {
return this.cachePrivate;
}
public void setCachePrivate(Boolean cachePrivate) {
this.customized = true;
this.cachePrivate = cachePrivate;
}
public Boolean getProxyRevalidate() {
return this.proxyRevalidate;
}
public void setProxyRevalidate(Boolean proxyRevalidate) {
this.customized = true;
this.proxyRevalidate = proxyRevalidate;
}
public Duration getStaleWhileRevalidate() {
return this.staleWhileRevalidate;
}
public void setStaleWhileRevalidate(Duration staleWhileRevalidate) {
this.customized = true;
this.staleWhileRevalidate = staleWhileRevalidate;
}
public Duration getStaleIfError() {
return this.staleIfError;
}
public void setStaleIfError(Duration staleIfError) {
this.customized = true;
this.staleIfError = staleIfError;
}
public Duration getSMaxAge() {
return this.sMaxAge;
}
public void setSMaxAge(Duration sMaxAge) {
this.customized = true;
this.sMaxAge = sMaxAge;
}
public CacheControl toHttpCacheControl() {
PropertyMapper map = PropertyMapper.get();
CacheControl control = this.createCacheControl();
PropertyMapper.Source var10000 = map.from(this::getMustRevalidate).whenTrue();
Objects.requireNonNull(control);
var10000.toCall(control::mustRevalidate);
var10000 = map.from(this::getNoTransform).whenTrue();
Objects.requireNonNull(control);
var10000.toCall(control::noTransform);
var10000 = map.from(this::getCachePublic).whenTrue();
Objects.requireNonNull(control);
var10000.toCall(control::cachePublic);
var10000 = map.from(this::getCachePrivate).whenTrue();
Objects.requireNonNull(control);
var10000.toCall(control::cachePrivate);
var10000 = map.from(this::getProxyRevalidate).whenTrue();
Objects.requireNonNull(control);
var10000.toCall(control::proxyRevalidate);
map.from(this::getStaleWhileRevalidate).whenNonNull().to((duration) -> {
control.staleWhileRevalidate(duration.getSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
map.from(this::getStaleIfError).whenNonNull().to((duration) -> {
control.staleIfError(duration.getSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
map.from(this::getSMaxAge).whenNonNull().to((duration) -> {
control.sMaxAge(duration.getSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
return control.getHeaderValue() == null ? null : control;
}
private CacheControl createCacheControl() {
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.noStore)) {
return CacheControl.noStore();
} else if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.noCache)) {
return CacheControl.noCache();
} else {
return this.maxAge != null ? CacheControl.maxAge(this.maxAge.getSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS) : CacheControl.empty();
}
}
private boolean hasBeenCustomized() {
return this.customized;
}
}
}
}
}
|
有缓存有关的常用配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
spring.web.resources.add-map=true
spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.max-age=3600
spring.web.resources.cache.use-last-modified=true
|
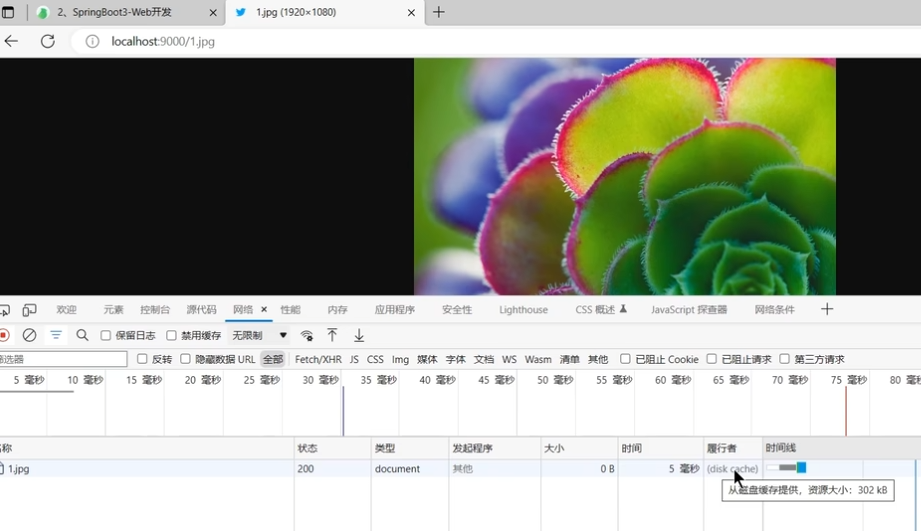 image-20250529090140010
image-20250529090140010
缓存相关参数在响应头中有所体现,Spring Boot
携带缓存等各种配置向浏览器发请求
Cache 相关的详细设置,在 Cachecontrol
类里,可以参考这个类进行更详细的配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class CacheControl {
@Nullable
private Duration maxAge;
private boolean noCache = false;
private boolean noStore = false;
private boolean mustRevalidate = false;
private boolean noTransform = false;
private boolean cachePublic = false;
private boolean cachePrivate = false;
private boolean proxyRevalidate = false;
@Nullable
private Duration staleWhileRevalidate;
@Nullable
private Duration staleIfError;
@Nullable
private Duration sMaxAge;
private boolean immutable = false;
protected CacheControl() {
}
。。。。。
}
|
缓存实现与配置
缓存实现方式之间的比较
- simple:默认的内存缓存,使用 ConcurrentHashMap
- 适合开发和测试环境
- 不支持分布式
- 性能较好,但不适合生产
- redis:分布式缓存
- ehcache:本地缓存
内存缓存(默认)
Spring Boot 默认使用简单的内存缓存:
1
2
3
| spring:
cache:
type: simple
|
Redis 缓存配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| spring:
cache:
type: redis
redis:
time-to-live: 600000 # 10分钟
cache-null-values: false
key-prefix: "myapp:"
use-key-prefix: true
data:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
database: 0
timeout: 2000ms
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 8
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 0
|
一般来说,如果需要自定义缓存配置,重写CacheConfig缓存配置类中的条目就可以
HTTP 缓存配置
静态资源缓存配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| spring:
web:
resources:
# 开启静态资源映射
add-mappings: true
# 静态资源位置
static-locations: classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/
# 缓存配置
cache:
# 使用 Last-Modified 头
use-last-modified: true
# 缓存控制
cachecontrol:
max-age: 3600 # 1小时
cache-public: true
must-revalidate: true
# 资源处理链
chain:
enabled: true
cache: true
compressed: true
strategy:
content:
enabled: true
paths:
|
使用Redis做集中式缓存
RedisTemplate
默认的缓存是在内存中定义HashMap,在实际的开发生产中,经常使用Redis作为缓存中间件,而不使用cache。
Redis
是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库、缓存和消息中间件。也是以key-value的形式进行存储数据的一款非关系型数据库。
通过Spring
Boot与Redis的集成,可以实现高效的分布式缓存解决方案。Spring Cache
抽象提供了简洁的注解方式,而 RedisTemplate
则提供了更灵活的操作方式。
Redis的Tempate 如下:
Redis的常用五大数据类型
- String【字符串】、List【列表】、Set【集合】、Hash【散列】、ZSet【有序集合】
分为两种
- 一种是
StringRedisTemplate
- 字符串专属:仅支持 String
类型的键值对操作,适合存储文本数据(如用户会话、配置信息)。专注于字符串操作,适合纯文本场景。
- 序列化简单:使用
StringSerializer,将字符串直接存储到
Redis,无需额外转换。
- 可读性高:Redis 中存储的键值可直接查看(如通过
redis-cli 命令)
- 另一种是
RedisTemplate
- 通用型模板:支持 Redis
所有数据类型(String、List、Set、Hash、ZSet),可存储任意 Java
对象。
- 灵活序列化:默认使用 Java 序列化(JDK
Serialization),也可自定义序列化方式(如 JSON 序列化)。
- 二进制存储:对象会被序列化为二进制数据,适合存储复杂结构(如用户对象、订单数据)。
两者对比
| 对比维度 |
StringRedisTemplate |
RedisTemplate |
| 默认序列化方式 |
StringSerializer(字符串序列化) |
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(Java 序列化) |
| 键(Key)类型 |
只能是 String 类型 |
可以是任意类型(需通过序列化转换) |
| 值(Value)类型 |
只能是 String 类型 |
可以是任意类型(需通过序列化转换) |
| 应用场景 |
纯文本数据(如配置项、简单字符串) |
复杂对象、集合数据(如 Java 对象、List、Set) |
| 序列化结果 |
直接存储字符串,可读性强 |
存储二进制数据,可读性差但效率高 |
并且Spring Boot会在侦测到存在 Redis 的依赖并且 Redis
的配置是可用的情况下,还可以使用RedisCacheManager初始化CacheManager。
实际例子
下面写一个例子
首先需要在pom.xml中添加Redis和Spring Cache的依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</version>
</dependency>
|
配置Redis
在application.yml中配置Redis缓存信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
password:
database: 0
cache:
type: redis
redis:
time-to-live: 60000
key-prefix: CACHE_
use-key-prefix: true
cache-null-values: false
|
启用缓存
在主应用类上添加@EnableCaching注解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
基本缓存操作
在Service层使用缓存注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| @Service
public class ProductService {
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#id")
public Product getProductById(Long id) {
System.out.println("Fetching product from database...");
return new Product(id, "Product " + id, 99.99);
}
@CachePut(value = "products", key = "#product.id")
public Product updateProduct(Product product) {
System.out.println("Updating product in database...");
return product;
}
@CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "#id")
public void deleteProduct(Long id) {
System.out.println("Deleting product from database...");
}
@Caching(evict = {
@CacheEvict(value = "products", allEntries = true)
})
public void clearAllCache() {
System.out.println("Clearing all products cache...");
}
}
|
可以自定义Redis缓存配置以更好地控制缓存行为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| @Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisCacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10))
.disableCachingNullValues()
.prefixCacheNameWith("CACHE_")
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.withInitialCacheConfigurations(getCacheConfigurations())
.transactionAware()
.build();
}
private Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> getCacheConfigurations() {
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> cacheConfigurations = new HashMap<>();
cacheConfigurations.put("products",
RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)));
cacheConfigurations.put("users",
RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer())));
return cacheConfigurations;
}
}
|







