安全与便利的天平往往难以把握——过于宽松的配置可能导致敏感数据泄露,过于严格的策略又会影响正常业务交互
什么是跨域?为什么会有跨域?
同源策略
其实这是一个很简单的东西,但是配置不好确实很容易让人头疼
CORS 的出现是为了解决浏览器的同源策略限制,我们先从同源策略说起
浏览器这样定义的同源:两个 URL 的协议、域名(主机名)、端口三者完全相同,才被视为 同源。
所以说,在开发前后端分离的项目的时候,由于前端项目和后端项目运行在不同的端口上,天然跨域产生了,配置不好的话经常会出现这种导致的500的问题,浏览器发起请求时,请求会发送出去,服务器也会处理并返回,但是浏览器会在门口把响应拦截下来并报错,不让前端 JS 代码拿到数据。
同源策略其实是浏览器的一种安全机制,防止恶意网站通过 JavaScript 获取另一个网站的敏感数据(比如 cookie、localStorage、API 返回的用户信息)。如果没有同源策略,黑客可以轻易伪造用户请求,窃取数据。
浏览器默认遵循同源策略。它规定:A 网站的 JavaScript (如 localhost:3000) 只有在和 B 网站 (如 localhost:8080) 同源的情况下,才能读取 B 返回的数据。
CORS 机制
CORS 是一套 HTTP 协议机制,是W3C 标准。它允许服务器告诉浏览器:“我是自愿把数据给这个域名的,别拦截了,浏览器大人放过我”。
这主要通过 HTTP 响应头 来控制:
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin: 允许哪些域名访问(例如 http://localhost:3000)。
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods: 允许哪些 HTTP 方法(GET, POST, PUT…)。
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers: 允许携带哪些头信息(Authorization, Content-Type…)。
- Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: 是否允许携带 Cookie/认证信息。
它允许浏览器向跨域的服务器发送请求,并让服务器决定是否允许这个跨域请求,是同源策略的安全扩展。
而且,CORS 的核心是服务器端配置,浏览器会根据服务器返回的响应头,判断是否允许当前页面的跨域请求。
浏览器行为
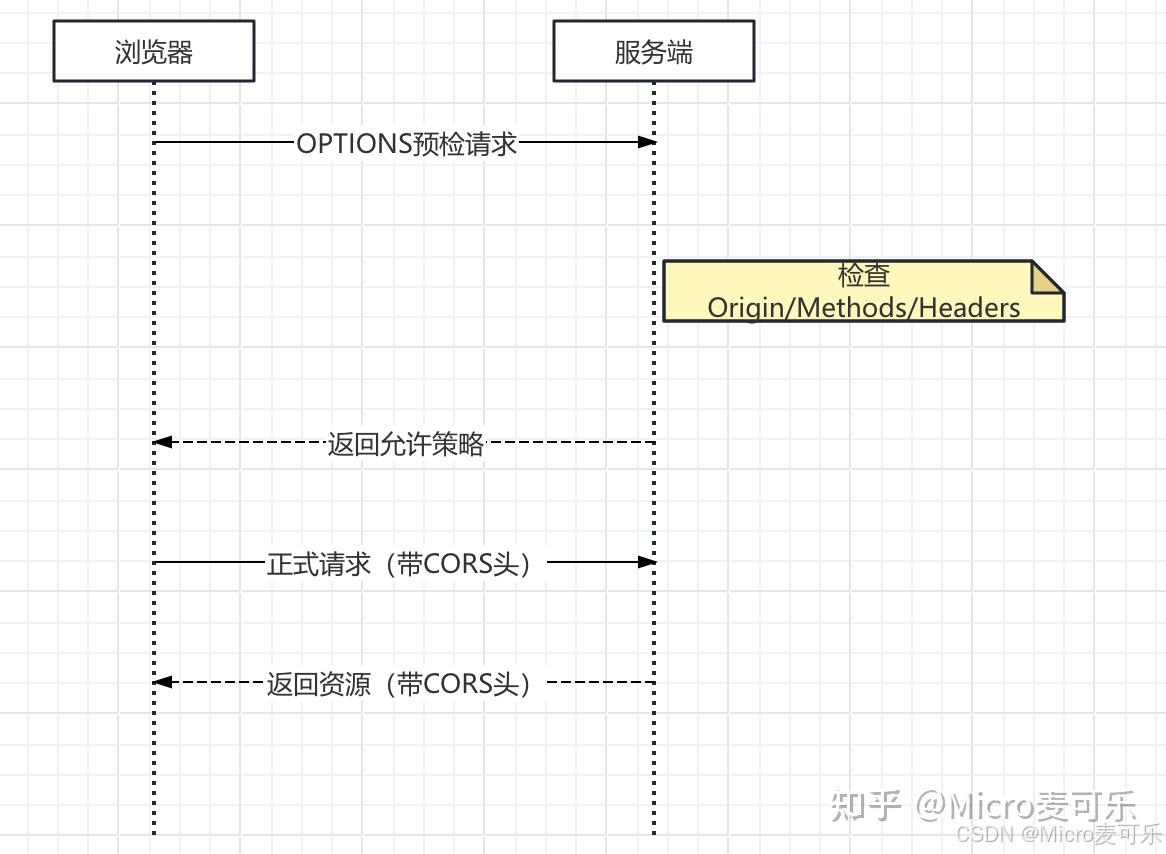
很多时候报错是因为不懂浏览器的预检请求(Preflight Request)机制。
浏览器将跨域请求分为两类:
简单请求
满足以下所有条件的请求为简单请求:
- 请求方法是以下三种之一:
GET、HEAD、POST - 请求头仅包含以下允许的头信息:
Accept、Accept-Language、Content-Language、Content-Type(仅允许application/x-www-form-urlencoded、multipart/form-data、text/plain)
那么简单请求的处理如下:
- 浏览器直接发送跨域请求,请求头中会自动添加
Origin字段(表示当前请求的源,如http://localhost:3000)。 - 服务器收到请求后,返回的响应头中会包含
Access-Control-Allow-Origin等 CORS 相关头。 - 浏览器检查响应头:如果
Access-Control-Allow-Origin包含当前源(或为*),则允许页面获取响应数据;否则,浏览器会拦截响应,抛出跨域错误(注意:此时服务器已经处理了请求,只是浏览器拦截了响应,是一个特殊的500)。
预检请求
不满足简单请求条件的请求,会触发预检请求(也叫 OPTIONS 请求),这是浏览器的 “提前询问” 机制,这个请求不带 Body,不带 Token,只是询问服务器:“我能发这个请求吗?”
- 如果服务器对 OPTIONS 回复 200 OK 且带上允许的 Header,浏览器才会发第二次真正的业务请求。
- 如果服务器拦截了 OPTIONS 请求(比如因为没有 Token 报了 401/403),CORS 失败。
例如,请求方法是PUT/DELETE、请求头包含Authorization/Content-Type: application/json、自定义头(如X-Token)。
那么预检请求是如何处理的:
- 浏览器先发送一个
OPTIONS请求(预检请求),包含以下关键头:Origin:当前请求的源。Access-Control-Request-Method:后续要发送的真实请求的方法(如PUT)。Access-Control-Request-Headers:后续要发送的真实请求的自定义头(如Content-Type, X-Token)。
- 服务器收到预检请求后,需要返回包含以下 CORS
头的响应,告知浏览器是否允许该跨域请求:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:允许的源。Access-Control-Allow-Methods:允许的请求方法。Access-Control-Allow-Headers:允许的请求头。Access-Control-Max-Age:预检请求的缓存时间(单位:秒),缓存期间无需重复发送预检请求。
- 如果服务器的响应满足要求,浏览器才会发送真实的请求;否则,浏览器直接抛出跨域错误,不会发送真实请求。
什么叫预检请求的 galgame 场景
- 浏览器:“服务器你好,我等会儿想发一个带 Authorization 头的 POST 请求,你允许吗?” (这是 OPTIONS 请求)
- 服务器:“允许,发吧。” (返回 200 OK + CORS Headers)
- 浏览器:“好的,这是真正的 POST 请求。” (这才是你的业务请求)
注意:OPTIONS 请求是不带 Token 的!
如果你的 Spring Security 过滤器链配置得太严,它一看:“哟,这个 OPTIONS 请求没带 Token?401 滚粗!
浏览器收到了 401,认为服务器不允许跨域,直接报错。你的业务代码(Controller)连执行的机会都没有。
附带凭据的请求
总所周知两种包含第三种))))))))
其实只是我习惯单拿出来,因为它的配置确实不太一样
实际上,经常出现 CR ,也就是Credentials Request,如果如果前端请求需要携带凭据(如 cookie、HTTP 认证信息、Token 在 cookie 中),需要满足:
- 前端需要在请求中设置
withCredentials: true,如 Axios 中axios.defaults.withCredentials = true - 服务器这边响应头中必须设置
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true,且Access-Control-Allow-Origin不能是\*(必须是具体的源,如http://localhost:3000)。
Spring Security如何配置服务端跨域
Spring Security 过滤器链中配置 CORS
在 Spring Security 7 (以及 6.x) 中,配置风格全面转向了 Lambda DSL。
很多人在 Spring MVC 层(比如用 @CrossOrigin 注解或
WebMvcConfigurer)配了 CORS,结果还是报 403。
因为 Spring Security 的过滤器链(Filter Chain)执行顺序在 Spring MVC 之前。如果请求在 Security 这一层被拦下了,MVC 层根本收不到请求,配置自然无效。
所以,必须在 Spring Security 过滤器链中配置 CORS。
存在这样的一个标准配置模板
1 | import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; |
这段代码做了两件事:
定义规则 (
CorsConfigurationSource):告诉 Spring 哪些域是合法的。挂载过滤器 (
http.cors(...)):Spring Security 会在过滤器链的最顶端加一个CorsFilter。这个之前的过滤器链顺序中提到过这件事当请求进来,CorsFilter 先检查。
如果是 OPTIONS 预检请求,CorsFilter 会直接基于你的规则返回 200 OK + CORS Headers,不会让请求继续走到后面的 AuthenticationFilter(认证过滤器)。
这样就避免了 “预检请求没有 Token 被 401 拦截” 的经典死循环。
注意,Postman 不遵守同源策略,它是开发者工具,不负责浏览器安全。不要用 Postman 测 CORS。一定要用浏览器(Chrome Network Tab)看 Response Headers。
配置 Spring Web 的 CORS
这回再讲如何配置 Spring Web 的 CORS
Spring Framework 自 4.2 起在 MVC
层面引入了对 CORS
的原生支持,可通过全局配置或注解方式开启
全局配置(WebMvcConfigurer)
1 |
|
实际上经常把 CORS 配置单拿出来进行全局配置
1 | import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; |
局部 CORS 配置(@CrossOrigin 注解)
适用于单个控制器或接口:
1 | import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin; |
别忘了,Spring Security 7 的过滤器链会优先于 CORS 过滤器执行,如果不配置,预检请求(OPTIONS)会被 Spring Security 拦截(比如被 CSRF、认证过滤器拦截),导致跨域失败。
前后端联合调试方案
假设前端部署在 https://frontend.app,后端 API 接口在
https://your-domain.com :
首先,在后端,我们需要明确告诉浏览器:“我信任
https://frontend.app,允许它带 Token
过来,也允许它读取数据。”
1 |
|
前端的主要任务是:携带正确的 Token 并在请求配置中开启凭证
1 | import axios from 'axios'; |
假设前端发起了一个 POST /api/user/profile 的请求。
观察预检请求 (Preflight / OPTIONS)
你会先看到一个名为 profile 的请求,方法是 OPTIONS。
状态码:必须是 200 OK (如果是 401/403,说明后端 Security 没配好)。
关键响应头 (Response Headers):
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://frontend.app (必须完全匹配)
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, …
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Authorization, Content-Type (必须包含你请求里带的头)
如果 OPTIONS 红了:
- 原因:Spring Security 拦截了 OPTIONS。
- 检查:确认 SecurityConfig 里 .cors(…) 是否调用,确认 CorsFilter 是否在 Filter 链中。
观察实际请求 (Actual Request)
如果 OPTIONS 成功了,紧接着会出现第二个 profile 请求,方法是 POST。
- Request Headers:必须包含 Authorization: Bearer xxx。
- Response Headers:同样必须包含
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://frontend.app
注意,实际中,有些情况下,如果后端直接抛出 500 异常,Spring 默认的错误处理机制可能不会加上 CORS 头,导致浏览器报 CORS 错误(掩盖了真实的 500 错误)。务必查看后端日志!







