在Spring项目中如何使用MongoDB
在Spring项目遇到什么需求需要用到MongoDB
首先,MongoDB 是 NoSQL,其次,它是文档型数据库,它拥有灵活
schema、高写入性能、适合非结构化 / 半结构化数据、水平扩展友好
一般在这样的情况下,我们考虑 MongoDB
存储非结构化 / 半结构化数据
所以说,当数据结构灵活多变(如用户行为日志、商品属性(不同商品字段差异大)、JSON
格式的 API
响应缓存等),传统关系型数据库的固定表结构会导致频繁的表结构变更,而
MongoDB 的文档模型(BSON
格式,支持嵌套结构)可直接存储动态字段,无需预先定义 schema。
存储日志等写入量大的场景
如日志系统(用户操作日志、系统运行日志)、物联网设备数据采集(传感器实时上报数据)等,需要高频写入且对事务性要求不高的场景。MongoDB
的写入性能优于多数关系型数据库,且支持分片集群实现水平扩展,应对高并发写入。
快速迭代的情况
当出现需求变更改很频繁(如电商的活动规则、内容平台的内容属性),使用
MongoDB
可避免因表结构调整导致的开发成本增加,加速迭代,而且丰富的查询语法和超级多内容的索引适合需要对数据进行多维度分析的场景,例如用户的行为分析,推荐内容计算
缓存或临时数据存储
那我们上面都说了,MongoDB 是
NoSQL,其次,它是文档型数据库,所以说,作为关系型数据库的补充,用它存储临时会话数据、API
请求缓存等,利用其高读写性能减轻主数据库压力是很好的
在Spring项目中使用MongoDB该做些什么
Spring 提供了Spring Data MongoDB模块,简化了 MongoDB
的操作,核心是通过MongoTemplate或Repository
接口 实现数据访问。
Spring Data MongoDB的核心依赖是这个
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId > </dependency >
然后在配置文件中进行配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 在application.yml中配置连接信息:spring: data: mongodb: uri: mongodb://localhost:27017/testdb
跟其他数据库类似,Spring Data MongoDB
提供两种主要操作方式:Repository
接口 (推荐,简化代码)和MongoTemplate(更灵活,适合复杂操作)。
所以他也能完美支持
JPA,通过定义接口继承MongoRepository,自动生成 CRUD
方法,无需手动实现。
继承MongoRepository<实体类, 主键类型>,自动获得基础
CRUD 方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;import java.util.List;public interface UserRepository extends MongoRepository <User, String> { List<User> findByAgeGreaterThan (Integer age) ; List<User> findByNameLike (String name) ; User findByAddressCity (String city) ; }
在实体类的定义中,只不过是使用@Document指定集合名(类似表名),@Id指定主键
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;@Document(collection = "users") public class User { @Id private String id; private String name; private Integer age; private List<String> hobbies; private Address address; } class Address { private String city; private String street; }
而MongoTemplate提供更底层的
API,支持复杂查询、聚合、索引操作等,适合 Repository
接口无法满足的场景。
Spring Boot 自动配置MongoTemplate,直接注入即可:
1 2 @Autowired private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
举几个常见操作大家就知道这东西跟别的其实很像了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 User user = new User ("张三" , 20 , Arrays.asList("篮球" , "游戏" ), new Address ("北京" , "朝阳路" ));mongoTemplate.insert(user); Query query = new Query ();query.addCriteria(Criteria.where("age" ).gt(18 ).lt(30 )) .addCriteria(Criteria.where("hobbies" ).in("篮球" )); List<User> users = mongoTemplate.find(query, User.class, "users" ); Aggregation aggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation( Aggregation.group("address.city" ).count().as("userCount" ), Aggregation.sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "userCount" ), Aggregation.limit(5 ) ); AggregationResults<CityCount> results = mongoTemplate.aggregate( aggregation, "users" , CityCount.class ); List<CityCount> cityCounts = results.getMappedResults(); mongoTemplate.indexOps("users" ).ensureIndex(new Index ().on("name" , Sort.Direction.ASC).unique());
前面也说过,MongoDB 4.0 + 支持事务,Spring
中通过@Transactional注解开启(需配置事务管理器MongoTransactionManager)。
也可以在通过@Indexed注解在实体类字段上定义索引,或使用IndexOperations手动创建。
MongoDB 也可以直接支持 JPA 的分页,Repository
接口也支持Pageable参数,
1 Page<User> findByAge (Integer age, Pageable pageable) ;
实际项目演示如何集成
MongoDB 到我们的项目中
之前我们在学习 MinIO 的时候,有个类似图片存储的 galgame
表情包的项目,我们继续扩展这个,添加评论的相关内容,使用 mongodb
存储评论内容(业务较多情况下,你还要用mysql去存储评论的有关元数据)
准备工作
在 pom.xml 中添加MongoDB依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > joda-time</groupId > <artifactId > joda-time</artifactId > <version > 2.12.5</version > </dependency >
在 src/main/resources/application.properties 中添加MongoDB配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 spring.data.mongodb.host =localhost spring.data.mongodb.port =27017 spring.data.mongodb.database =ergou_gallery_db spring.data.mongodb.max-connection-idle-time =60000 spring.data.mongodb.max-connection-life-time =120000
数据库设计
我们设计这样一个数据库 ergou_gallery_db
image-20251029200134090
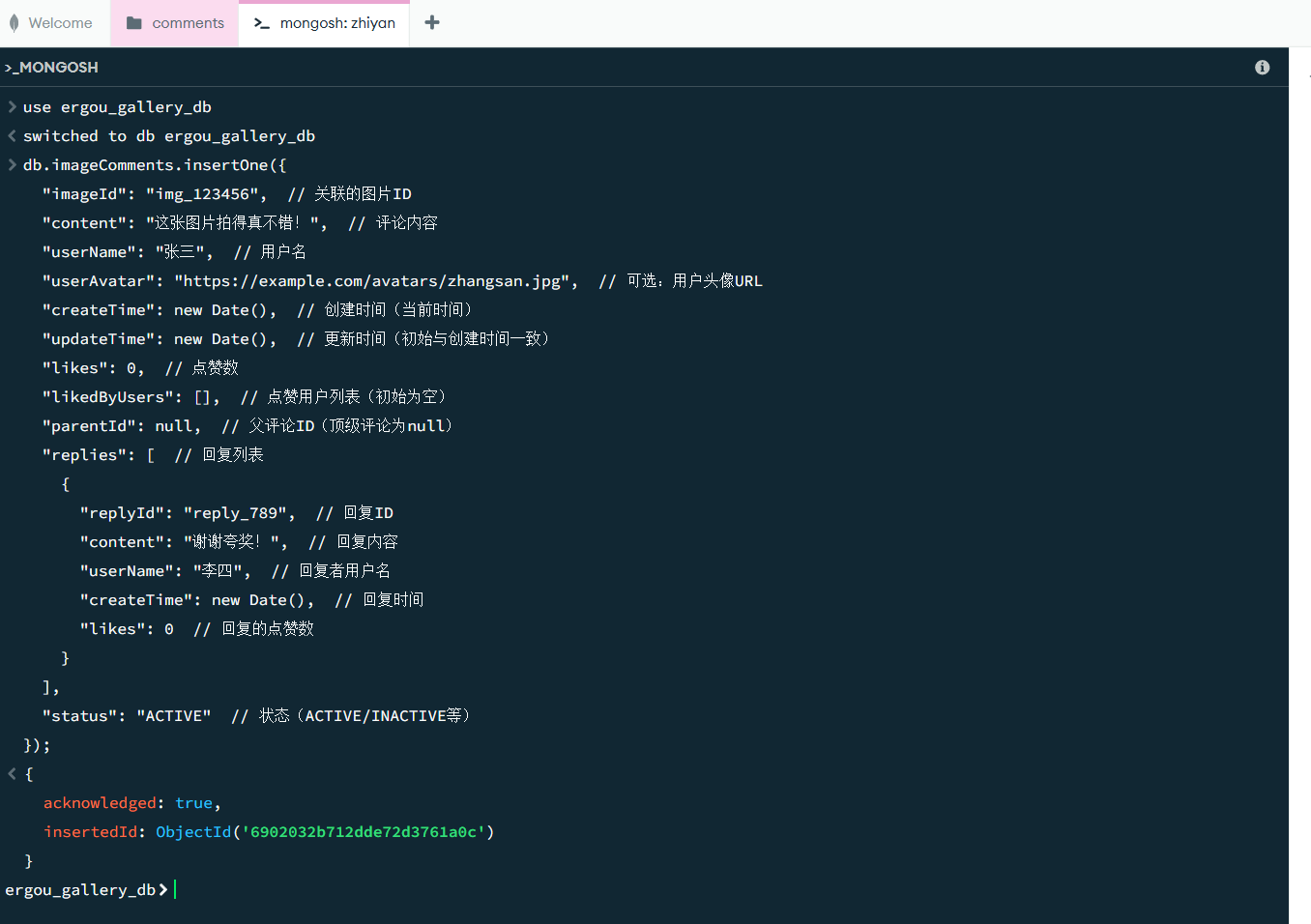
添加一个评论的集合,comments,设计这样的文档结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 { "_id" : "ObjectId(自动生成)" , "imageId" : "图片ID(关联ImageInfo的id)" , "content" : "评论内容" , "userName" : "用户名" , "userAvatar" : "用户头像URL(可选)" , "createTime" : "创建时间" , "updateTime" : "更新时间" , "likes" : 0 , "likedByUsers" : [ "user1" , "user2" ] , "parentId" : null , "replies" : [ { "replyId" : "回复ID" , "content" : "回复内容" , "userName" : "回复者" , "createTime" : "回复时间" , "likes" : 0 } ] , "status" : "ACTIVE" }
image-20251029200608991
表设计没什么说道,最重要的是设计索引
索引可以大幅提升查询性能。在评论系统中,我们经常需要:
按图片ID查询评论
按时间排序
查询特定用户的评论
我们这样设计几个索引
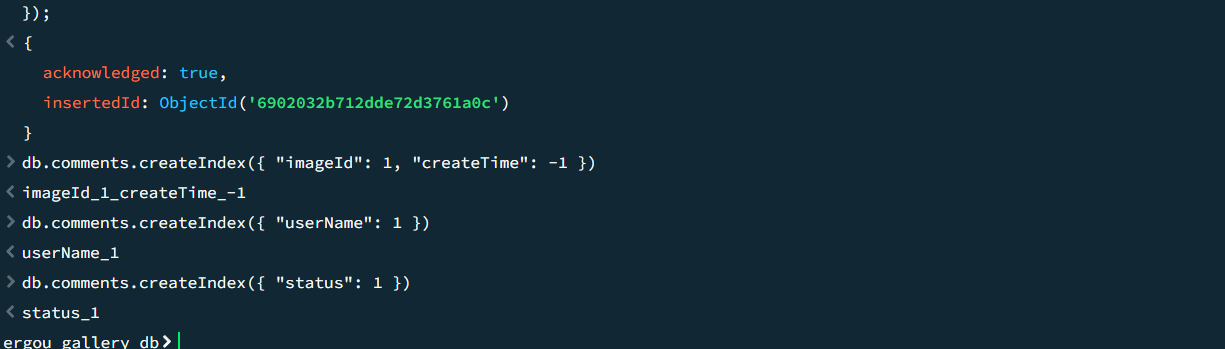
复合索引(最重要):
1 db.comments .createIndex ({ "imageId" : 1 , "createTime" : -1 })
用途:按图片查询评论并按时间倒序排列
imageId: 1:升序
createTime: -1:降序
单字段索引:
1 db.comments .createIndex ({ "userName" : 1 })
状态索引
1 db.comments .createIndex ({ "status" : 1 })
还可以这样设计一个 TTL 索引
1 db.comments .createIndex ({ "createTime" : 1 }, { expireAfterSeconds : 31536000 })
自动删除一年前的评论,在这里就是演示一下,没人会这样写业务的))
image-20251029200627820
创建MongoDB配置类
这个类更多是讲解,因为上面我们创建了集合和索引,再运行这个会冲突
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 package hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.config;import com.mongodb.client.MongoClient;import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoTemplate;import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.Index;import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.IndexOperations;@Slf4j @Configuration @RequiredArgsConstructor public class MongoConfig { private final MongoTemplate mongoTemplate; private final MongoClient mongoClient; @PostConstruct public void initIndexes () { log.info("开始初始化MongoDB索引..." ); try { IndexOperations indexOps = mongoTemplate.indexOps("comments" ); Index imageTimeIndex = new Index () .on("imageId" , org.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Direction.ASC) .on("createTime" , org.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Direction.DESC) .named("idx_imageId_createTime" ); indexOps.createIndex(imageTimeIndex); log.info("创建索引: idx_imageId_createTime" ); Index userIndex = new Index () .on("userName" , org.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Direction.ASC) .named("idx_userName" ); indexOps.createIndex(userIndex); log.info("创建索引: idx_userName" ); Index statusIndex = new Index () .on("status" , org.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Direction.ASC) .named("idx_status" ); indexOps.createIndex(statusIndex); log.info("创建索引: idx_status" ); log.info("MongoDB索引初始化完成!" ); MongoDatabase database = mongoClient.getDatabase("ergou_gallery_db" ); log.info("已连接到MongoDB数据库: {}" , database.getName()); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("MongoDB索引创建失败: {}" , e.getMessage(), e); } } }
这个配置类很神经就是了,写主要还是想说一下其中的方法
其中,涉及到了两个 MongoDB 操作的核心对象
MongoTemplateMongoClient
@PostConstruct大伙应该不陌生,类实例化后、依赖注入完成时自动执行 ,创建索引,其中
然后验证数据库连接就是 get 方法,通过
mongoClient.getDatabase("数据库名")
获取数据库对象,验证是否成功连接到名为 ergou_gallery_db
的数据库。
创建实体类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 package hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.entity;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.Data;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Field;import java.time.LocalDateTime;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;@Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Document(collection = "comments") public class Comment { @Id private String id; @Field("imageId") private String imageId; @Field("content") private String content; @Field("userName") private String userName; @Field("userAvatar") private String userAvatar; @Field("createTime") private LocalDateTime createTime; @Field("updateTime") private LocalDateTime updateTime; @Field("likes") private Integer likes = 0 ; @Field("likedByUsers") private List<String> likedByUsers = new ArrayList <>(); @Field("parentId") private String parentId; @Field("replies") private List<Reply> replies = new ArrayList <>(); @Field("status") private CommentStatus status = CommentStatus.ACTIVE; public enum CommentStatus { ACTIVE, DELETED, HIDDEN } @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public static class Reply { private String replyId; private String content; private String userName; private String userAvatar; private LocalDateTime createTime; private Integer likes = 0 ; private List<String> likedByUsers = new ArrayList <>(); } }
没啥好说的
repository类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 package hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.repository;import hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.entity.Comment;import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.Query;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import java.time.LocalDateTime;import java.util.List;@Repository public interface CommentRepository extends MongoRepository <Comment, String> { List<Comment> findByImageIdAndStatusOrderByCreateTimeDesc (String imageId, Comment.CommentStatus status) ; Page<Comment> findByImageIdAndStatus (String imageId, Comment.CommentStatus status, Pageable pageable) ; List<Comment> findByUserNameAndStatus (String userName, Comment.CommentStatus status) ; long countByImageIdAndStatus (String imageId, Comment.CommentStatus status) ; @Query("{ 'createTime': { $gte: ?0, $lte: ?1 }, 'status': ?2 }") List<Comment> findCommentsByTimeRange (LocalDateTime startTime, LocalDateTime endTime, Comment.CommentStatus status) ; @Query("{ 'imageId': ?0, 'likes': { $gte: ?1 }, 'status': ?2 }") List<Comment> findHotComments (String imageId, Integer minLikes, Comment.CommentStatus status) ; void deleteByImageId (String imageId) ; }
这个可得好好说说,Mongodb 的 repository 类 和 mysql
比较像,但是还是得说一下
该接口继承了
MongoRepository<Comment, String>,其中:
Comment:操作的实体类(对应 MongoDB 中的集合
comments)。String:实体类主键(_id)的类型。
通过继承
MongoRepository,无需手动实现,就可以直接使用大量内置方法(如
save()、findById()、delete()
等)。这些内容和命名规则和 mysql 的区别不大
MongoDB 可以通过方法命名规则 或
@Query 注解
维度
MongoDB Repository
MySQL Repository(JPA)
数据模型 操作文档(Document) ,对应 MongoDB
集合(Collection)
操作实体(Entity) ,对应 MySQL 表(Table)
主键 默认使用 _id 字段(ObjectId 类型),自动生成
通常使用 @Id 标注自定义主键(如自增 ID)
查询语法 基于 MongoDB 的查询语法(如
$gte、$lte)
基于 SQL 语法(如
WHERE、AND、LIKE)
关联关系 不支持外键,通过嵌套文档(如 replies
字段)或引用实现关联
支持外键(@ManyToOne 等注解),通过 JOIN 关联表
方法命名规则 支持大部分相同规则,但部分关键词适配文档结构(如
And、Or、In)
基于表字段和 SQL 操作(如
Like、Between)
自定义查询注解 使用 @Query 编写 MongoDB JSON 格式查询
使用 @Query 编写 SQL 语句
Spring Data MongoDB
会根据方法名自动解析查询条件,无需手动编写查询语句。核心规则和 mysql
的一样:
方法名格式:动作(find/delete/count)+ 条件(By字段 + 关键字)+ 排序/分页。
支持的关键字:And、Or、In、NotIn、Like、GreaterThan、LessThan、OrderBy
等。
当查询条件复杂(如范围查询、嵌套字段查询)时,用 @Query
注解直接编写 MongoDB 的查询 JSON,更灵活。这个思路是和 mysql 一样的
默认情况下,实体类名 Comment 会映射到 MongoDB 的集合
comments(小写复数)。若需自定义集合名,在实体类上用
@Document(collection = "自定义名称") 标注。
而且这里的 repository 也是通过通过 Pageable
参数实现分页和排序,例如:
1 2 3 Page<Comment> findByStatus (Comment.CommentStatus status, Pageable pageable) ;
Repository方法命名规则说明:
findBy…:查询方法
countBy…:统计方法
deleteBy…:删除方法
And、Or:连接多个条件
OrderBy…Desc/Asc:排序
创建 Service 层
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 package hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.service.impl;import hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.entity.Comment;import hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.repository.CommentRepository;import hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.service.CommentService;import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.time.LocalDateTime;import java.util.List;import java.util.UUID;@Slf4j @Service @RequiredArgsConstructor public class CommentServiceImpl implements CommentService { private final CommentRepository commentRepository; @Override public Comment addComment (String imageId, String content, String userName, String userAvatar) { log.info("添加评论 - 图片ID: {}, 用户: {}" , imageId, userName); Comment comment = new Comment (); comment.setImageId(imageId); comment.setContent(content); comment.setUserName(userName); comment.setUserAvatar(userAvatar); comment.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); comment.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); comment.setStatus(Comment.CommentStatus.ACTIVE); return commentRepository.save(comment); } @Override public Comment addReply (String commentId, String content, String userName, String userAvatar) { log.info("添加回复 - 评论ID: {}, 用户: {}" , commentId, userName); Comment comment = commentRepository.findById(commentId) .orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException ("评论不存在" )); Comment.Reply reply = new Comment .Reply(); reply.setReplyId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); reply.setContent(content); reply.setUserName(userName); reply.setUserAvatar(userAvatar); reply.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); comment.getReplies().add(reply); comment.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); return commentRepository.save(comment); } @Override public List<Comment> getCommentsByImageId (String imageId) { log.info("查询图片评论 - 图片ID: {}" , imageId); return commentRepository.findByImageIdAndStatusOrderByCreateTimeDesc( imageId, Comment.CommentStatus.ACTIVE); } @Override public Page<Comment> getCommentsByImageIdWithPage (String imageId, int page, int size) { log.info("分页查询图片评论 - 图片ID: {}, 页码: {}, 大小: {}" , imageId, page, size); PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(page, size, Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "createTime" )); return commentRepository.findByImageIdAndStatus( imageId, Comment.CommentStatus.ACTIVE, pageRequest); } @Override public Comment likeComment (String commentId, String userName) { log.info("点赞评论 - 评论ID: {}, 用户: {}" , commentId, userName); Comment comment = commentRepository.findById(commentId) .orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException ("评论不存在" )); if (!comment.getLikedByUsers().contains(userName)) { comment.getLikedByUsers().add(userName); comment.setLikes(comment.getLikes() + 1 ); comment.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); return commentRepository.save(comment); } return comment; } @Override public Comment unlikeComment (String commentId, String userName) { log.info("取消点赞 - 评论ID: {}, 用户: {}" , commentId, userName); Comment comment = commentRepository.findById(commentId) .orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException ("评论不存在" )); if (comment.getLikedByUsers().remove(userName)) { comment.setLikes(Math.max(0 , comment.getLikes() - 1 )); comment.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); return commentRepository.save(comment); } return comment; } @Override public void deleteComment (String commentId) { log.info("删除评论 - 评论ID: {}" , commentId); Comment comment = commentRepository.findById(commentId) .orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException ("评论不存在" )); comment.setStatus(Comment.CommentStatus.DELETED); comment.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); commentRepository.save(comment); } @Override public long getCommentCount (String imageId) { return commentRepository.countByImageIdAndStatus(imageId, Comment.CommentStatus.ACTIVE); } @Override public List<Comment> getHotComments (String imageId, int minLikes) { log.info("查询热门评论 - 图片ID: {}, 最小点赞数: {}" , imageId, minLikes); return commentRepository.findHotComments(imageId, minLikes, Comment.CommentStatus.ACTIVE); } }
接口略,只写了服务类,实际上,Mongodb 影响的只是持久层的内容,提供的
Service 层和 Controller 层,体现的地方只是在适配 MongoDB
特性的特殊设计
其中的评论位置,我写了一个回复
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Override public Comment addReply (String commentId, String content, String userName, String userAvatar) { Comment comment = commentRepository.findById(commentId) .orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException ("评论不存在" )); Comment.Reply reply = new Comment .Reply(); reply.setReplyId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); comment.getReplies().add(reply); return commentRepository.save(comment); }
MongoDB 支持 嵌套文档 (一个文档中包含另一个 /
多个文档), Comment 实体中包含
List<Reply> 嵌套结构,Service 层的
addReply 方法正是利用了这一特性:
和 MySQL 对比:若用 MySQL,需单独建 reply 表并通过
comment_id 关联,Service 层需分别操作 comment
表和 reply 表;而 MongoDB 直接在主文档中嵌套
replies 列表,只需更新主文档,操作更简洁。
注意点:嵌套文档默认没有独立的索引,若需频繁查询
“某用户的所有回复”,需在 Comment 实体的
replies.userName 字段上单独创建索引
点赞部分也是基于数组的去重更新,Comment 实体中的
likedByUsers(存储点赞用户列表)是 MongoDB
数组类型的典型应用,Service 层的
likeComment/unlikeComment
方法利用了数组的增删操作:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Override public Comment likeComment (String commentId, String userName) { Comment comment = commentRepository.findById(commentId).orElseThrow(...); if (!comment.getLikedByUsers().contains(userName)) { comment.getLikedByUsers().add(userName); comment.setLikes(comment.getLikes() + 1 ); return commentRepository.save(comment); } return comment; }
数组去重:MongoDB 本身支持 $addToSet
操作符(添加元素时自动去重),若想进一步优化,可在 Repository 层用
@Query 结合 $addToSet 实现原子操作,避免
Service 层的 contains 判断(减少内存操作):
1 2 3 @Query(value = "{ '_id': ?0 }", update = "{ $addToSet: { 'likedByUsers': ?1 }, $inc: { 'likes': 1 } }") void likeCommentAtomically (String commentId, String userName) ;
冗余字段:likes 是 likedByUsers
数组的长度冗余字段,目的是避免每次统计点赞数都要计算数组长度(likedByUsers.size()),提升查询性能(MongoDB
数组长度计算需遍历数组,冗余字段可直接读取)。
Service 层的 getCommentsByImageIdWithPage 方法使用
PageRequest 实现分页,底层依赖 MongoDB 的
游标分页 (而非 MySQL 的
LIMIT/OFFSET):
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Override public Page<Comment> getCommentsByImageIdWithPage (String imageId, int page, int size) { PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(page, size, Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "createTime" )); return commentRepository.findByImageIdAndStatus(imageId, Comment.CommentStatus.ACTIVE, pageRequest); }
和 MySQL 对比:MySQL 分页用
LIMIT size OFFSET (page*size),数据量大时会因跳过大量数据导致性能差;MongoDB
的游标分页通过索引有序遍历,性能更稳定(前提是 createTime
字段已创建索引,即之前 MongoConfig 中的
idx_imageId_createTime 复合索引)。
注意点:分页排序字段必须包含在索引中(如这里的
imageId + createTime
复合索引),否则会触发全集合扫描,导致分页性能下降。
创建接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 package hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.controller;import hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.entity.Comment;import hbnu.project.ergoutreegalemjstore.service.CommentService;import lombok.Data;import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;@Slf4j @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/comments") @RequiredArgsConstructor public class CommentController { private final CommentService commentService; @PostMapping public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> addComment (@RequestBody CommentRequest request) { try { Comment comment = commentService.addComment( request.getImageId(), request.getContent(), request.getUserName(), request.getUserAvatar() ); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , true ); response.put("message" , "评论添加成功" ); response.put("data" , comment); return ResponseEntity.ok(response); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("添加评论失败" , e); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , false ); response.put("message" , "评论添加失败: " + e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response); } } @PostMapping("/{commentId}/reply") public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> addReply ( @PathVariable String commentId, @RequestBody ReplyRequest request) { try { Comment comment = commentService.addReply( commentId, request.getContent(), request.getUserName(), request.getUserAvatar() ); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , true ); response.put("message" , "回复添加成功" ); response.put("data" , comment); return ResponseEntity.ok(response); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("添加回复失败" , e); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , false ); response.put("message" , "回复添加失败: " + e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response); } } @GetMapping("/image/{imageId}") public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> getComments (@PathVariable String imageId) { try { List<Comment> comments = commentService.getCommentsByImageId(imageId); long count = commentService.getCommentCount(imageId); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , true ); response.put("data" , comments); response.put("total" , count); return ResponseEntity.ok(response); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("获取评论失败" , e); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , false ); response.put("message" , "获取评论失败: " + e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response); } } @GetMapping("/image/{imageId}/page") public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> getCommentsWithPage ( @PathVariable String imageId, @RequestParam(defaultValue = "0") int page, @RequestParam(defaultValue = "10") int size) { try { Page<Comment> commentPage = commentService.getCommentsByImageIdWithPage(imageId, page, size); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , true ); response.put("data" , commentPage.getContent()); response.put("currentPage" , commentPage.getNumber()); response.put("totalPages" , commentPage.getTotalPages()); response.put("totalElements" , commentPage.getTotalElements()); return ResponseEntity.ok(response); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("分页获取评论失败" , e); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , false ); response.put("message" , "获取评论失败: " + e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response); } } @PostMapping("/{commentId}/like") public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> likeComment ( @PathVariable String commentId, @RequestBody LikeRequest request) { try { Comment comment = commentService.likeComment(commentId, request.getUserName()); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , true ); response.put("message" , "点赞成功" ); response.put("data" , comment); return ResponseEntity.ok(response); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("点赞失败" , e); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , false ); response.put("message" , "点赞失败: " + e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response); } } @PostMapping("/{commentId}/unlike") public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> unlikeComment ( @PathVariable String commentId, @RequestBody LikeRequest request) { try { Comment comment = commentService.unlikeComment(commentId, request.getUserName()); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , true ); response.put("message" , "取消点赞成功" ); response.put("data" , comment); return ResponseEntity.ok(response); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("取消点赞失败" , e); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , false ); response.put("message" , "取消点赞失败: " + e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response); } } @DeleteMapping("/{commentId}") public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> deleteComment (@PathVariable String commentId) { try { commentService.deleteComment(commentId); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , true ); response.put("message" , "评论删除成功" ); return ResponseEntity.ok(response); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("删除评论失败" , e); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , false ); response.put("message" , "删除评论失败: " + e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response); } } @GetMapping("/image/{imageId}/hot") public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> getHotComments ( @PathVariable String imageId, @RequestParam(defaultValue = "5") int minLikes) { try { List<Comment> hotComments = commentService.getHotComments(imageId, minLikes); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , true ); response.put("data" , hotComments); return ResponseEntity.ok(response); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("获取热门评论失败" , e); Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap <>(); response.put("success" , false ); response.put("message" , "获取热门评论失败: " + e.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response); } } @Data static class CommentRequest { private String imageId; private String content; private String userName; private String userAvatar; } @Data static class ReplyRequest { private String content; private String userName; private String userAvatar; } @Data static class LikeRequest { private String userName; } }
Controller 层作为接口层,主要负责接收请求、调用 Service
并返回响应,需特殊说明的也就是是 请求 / 响应 DTO 的设计
和 MongoDB 文档 ID 的处理
MongoDB 文档默认的 _id 字段(类型为
ObjectId),在代码中被映射为 Comment 实体的
String 类型 ID(通过 @Id 注解):
其实,这些设计也都大差不差了,也不算是新东西了
测试
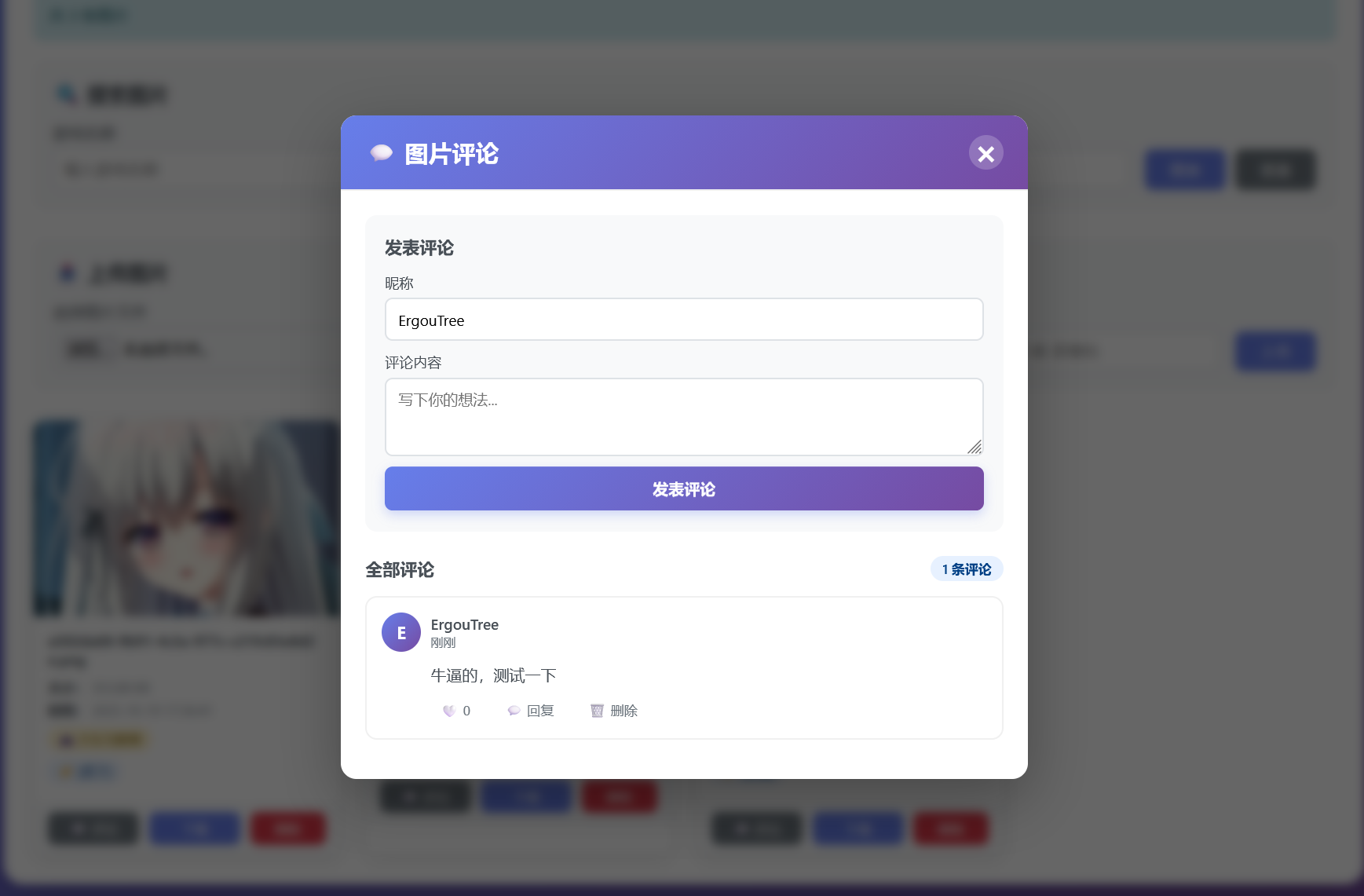
这次我修改了一下前端,我们测试一下
image-20251029204743989
业务这边是没有问题的
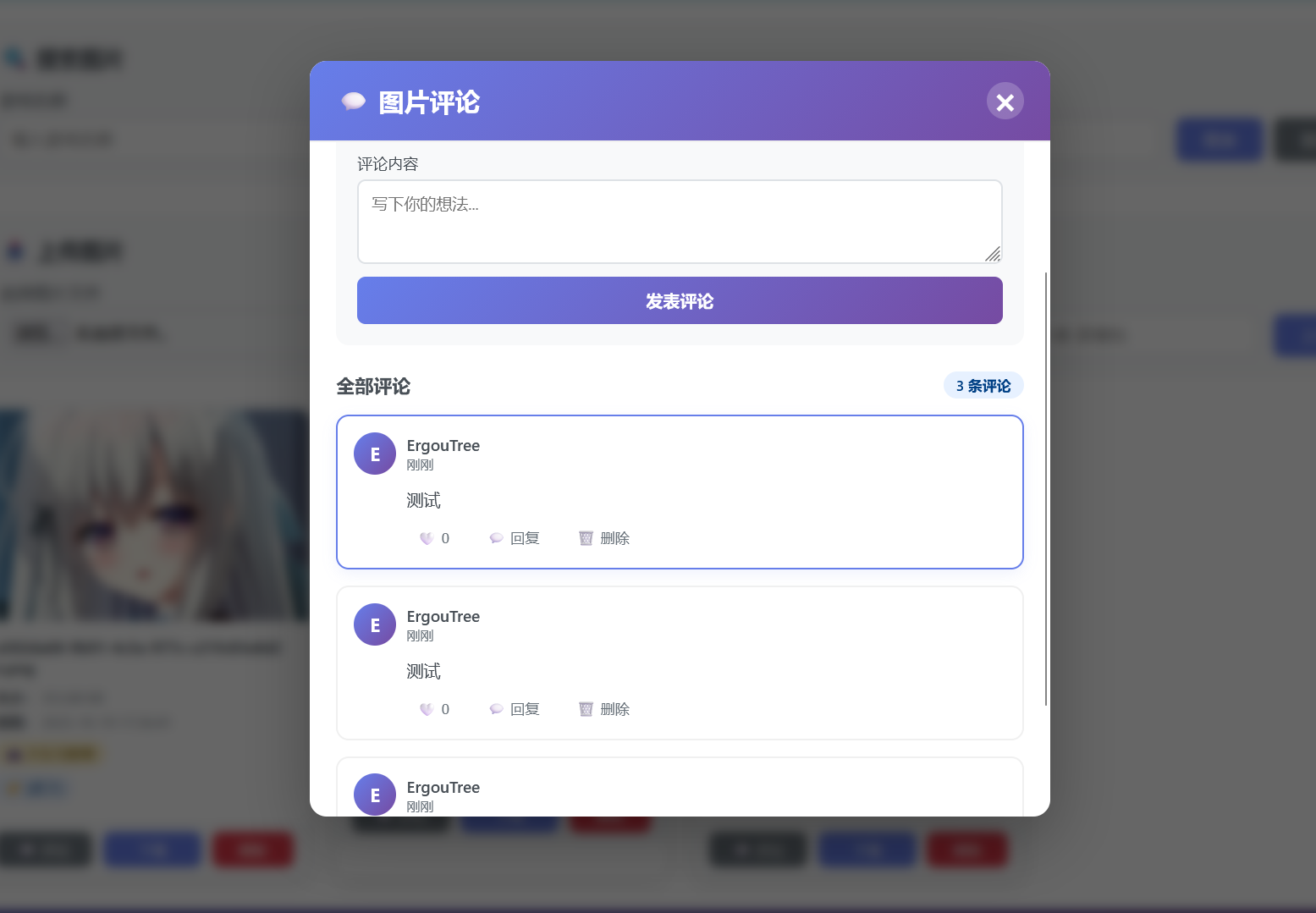
image-20251029204752009
多条的情况下也能按照索引正确排序
image-20251029204900403
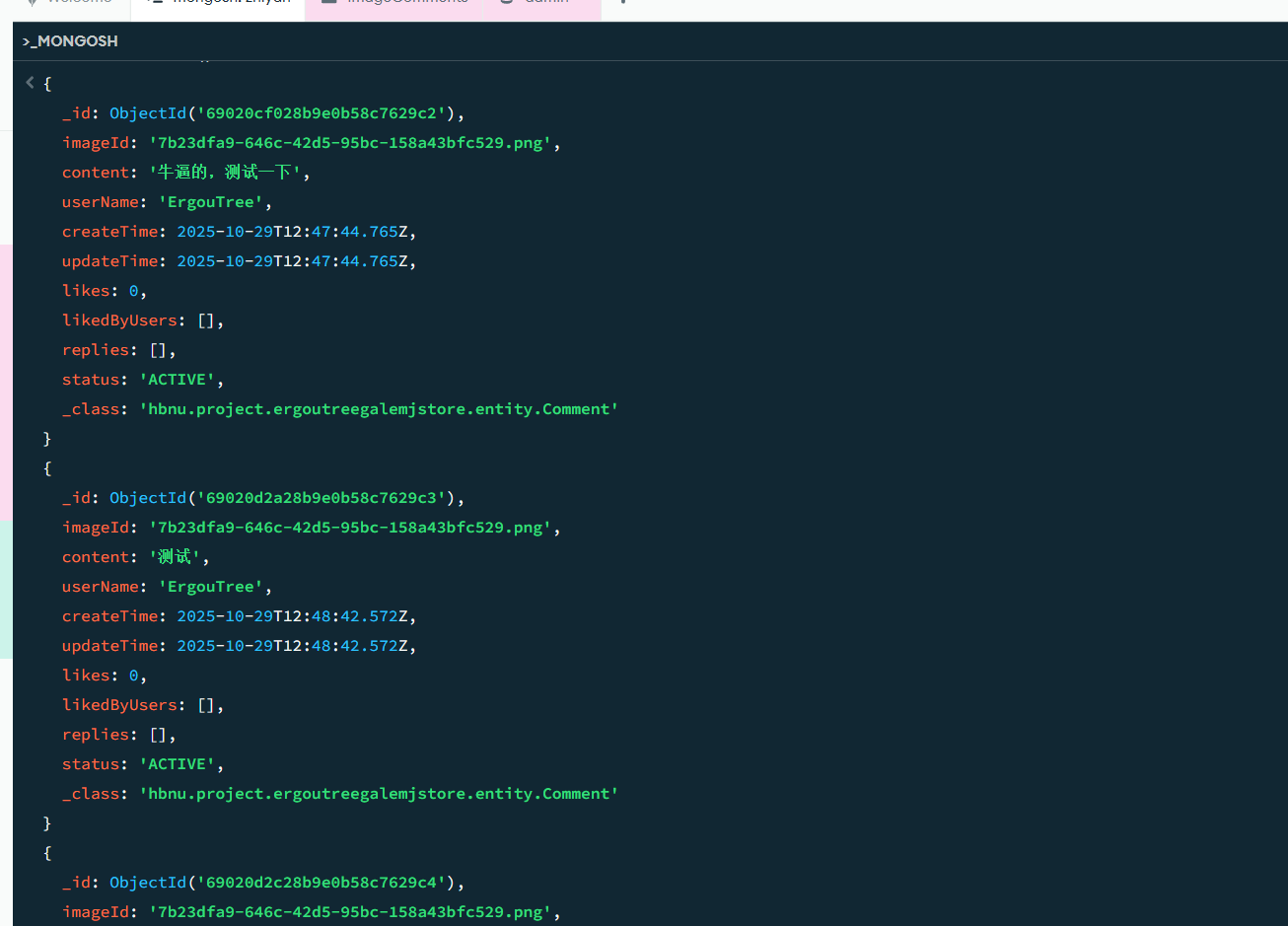
查一下mongodb这边看看持久化的状态
image-20251029205009383
没有问题
MongoDB 还是很简单好用的